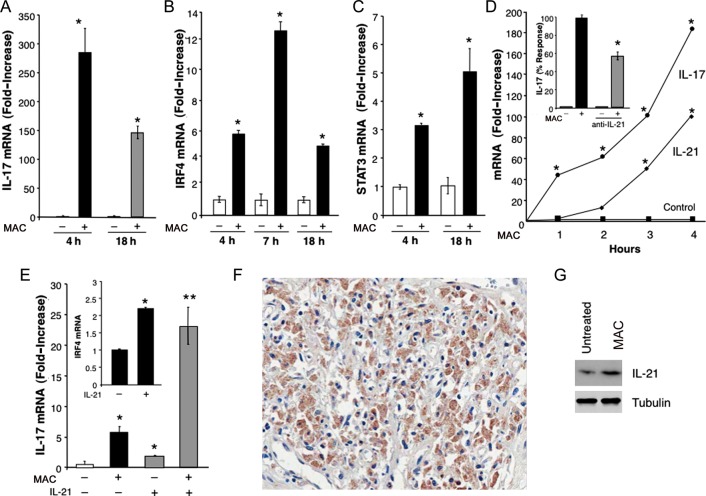
Figure 6.
Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) induces interleukin 17 (IL-17)–related transcription factors IRF4, STAT3, and interleukin 21 (IL-21). A, IL-17 messenger RNA (mRNA) levels in total mRNA from macrophages exposed to MAC (ratio, 10:1) for 4–18 hours (*P < .01; n = 3). B, Findings of kinetic transcriptional analysis of IRF4 mRNA in macrophage cultures incubated with MAC for various intervals (*P < .05; n = 3). C, STAT3 mRNA levels in macrophages that were or were not exposed to MAC (*P < .05; n = 3). D, Findings of kinetic transcriptional analysis of IL-21 and IL-17 by real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction in macrophage cultures incubated with MAC for 1–4 hours (*P < .01; n = 3). The inset shows findings for macrophages that were incubated with MAC overnight in the presence or absence of neutralizing IL-21 antibodies and evaluated for IL-17 transcription. Results are expressed as percentage response, compared with cultures that did not receive antibodies (*P < .05). E, IL-17 mRNA levels in macrophages exposed to MAC and/or IL-21 (10 ng/mL) for 4 hours (*P ≤ .05, **P < .01; n = 3). The inset shows IRF4 mRNA levels in macrophages that were exposed to IL-21 for 4 hours (*P < .05; n = 3). Data are for a representative donor. F, Immunohistochemical staining revealed IL-21–positive cells in lymph node tissue from an individual with AIDS who was coinfected with MAC and HIV-1. G, Whole cell protein extracts of macrophages exposed to MAC showed enhanced IL-21 protein expression, compared with unexposed cultures, as determined by Western blot (n = 3).