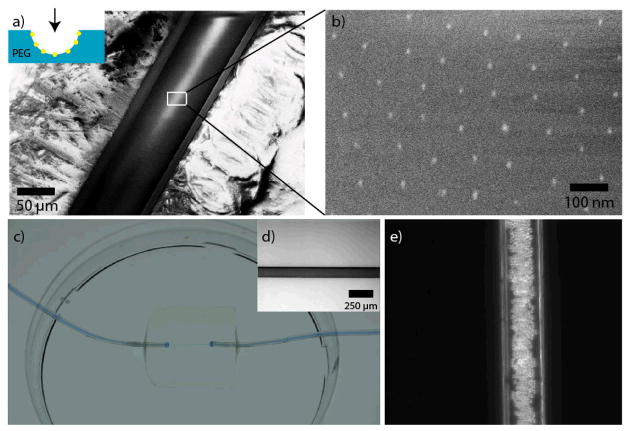
Figure 3.
Transfer of the nanoparticles onto the hydrogel channel’s surface and microfluidic setup. (a) Cryo-SEM-image of a cut hydrogel channel (the viewer’s perspective is shown in the inset). The transfer of the Au-NP patterns is shown in the magnified Cryo-SEM-image in (b). There were no changes in the nanparticle pattern compared to the original glass fiber. (c) The channels were incorporated into a 20 × 20 × 4 mm hydrogel and they were sealed to tubes serving as inlets and outlets. For visualization the channel was filled with blue ink. The whole hydrogel channel system was bonded to a petri dish filled with water to prevent drying out. (d) Bright-field microscopy image of a hydrogel channel (125 μm) filled with ink. (e) Phase contrast image of a hydrogel channel (125 μm ) with 10 μm-sized polystyrene beads flowing through the channel.