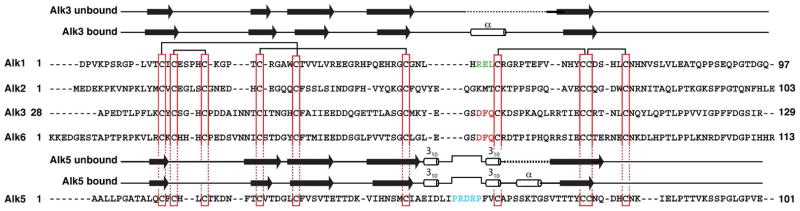
Figure 1.
Sequence alignment of the Alk1 extracellular domain with the extracellular domains of the BMP type I receptors Alk2, Alk3 and Alk6 and the TGF-β type I receptor, Alk5. Conserved cysteines (vertical red boxes) and disulphide bonds (horizontal black bars) in the Alk3 (19, 20), Alk5 (39, 40), and Alk6 (41) structures that define the receptor three finger toxin fold are highlighted. Functionally important residues in the helical region of Alk3 and Alk6 are highlighted in red, while those in the pre-helical extension of Alk5 are highlighted in cyan. Proposed functionally important residues in Alk1 are highlighted in green. Unbound and bound secondary structural elements shown above the Alk1, Alk2, Alk3, and Alk6 sequences correspond to those from the solution structure of Alk3 (PDB 2K3G) and the crystal structure of Alk3 bound to BMP-2 (PDB 1REW); those above the Alk5 sequence correspond to those from the solution structure of Alk5 (2L5S) and the crystal structure of Alk5 bound to the TGF-β3:TβR-II complex (PDB 2PJY).