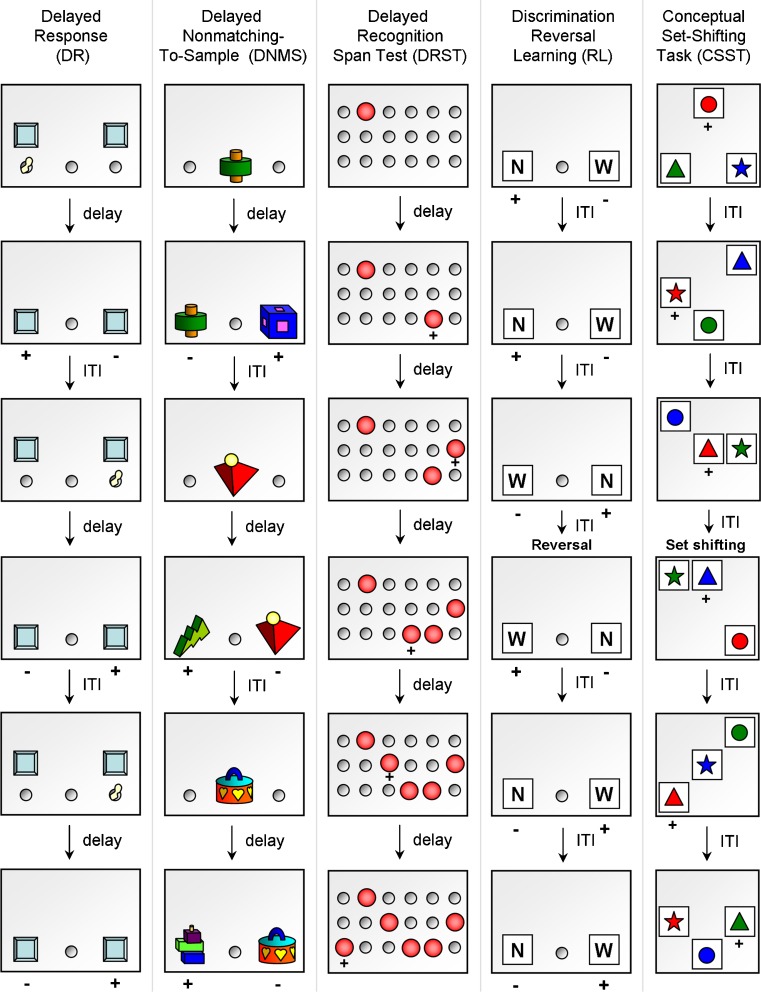
Fig. 1.
Schematic diagrams illustrating the cognitive tests sensitive to aging. DR is a spatial working memory test in which the subject has to remember the spatial location of a cued object through a delay period (during which an opaque screen hides the stimulus tray). In DNMS test of visual recognition memory, the subject is presented with a sample object, and after a delay interval, the subject must choose the novel object when presented together with the sample object. The spatial version of DRST assesses recognition and spatial working memory and requires the subject to identify a novel stimulus among an increasing array of previously presented stimuli. Discrimination RL is used to measure set-shifting ability, a component of executive function. Illustrated is the pattern version of discrimination RL, in which the subject learns to associate one of the patterns (N) with reward. After the subject achieves the accuracy criterion, discrimination reversal is initiated where the previously unrewarded stimulus (W) becomes the rewarded stimulus. CSST assesses executive functions such as abstraction and set-shifting. In CSST, the subject is rewarded when choosing the correct color (red), regardless of shape. After the subject chooses the correct stimulus consecutively, the rewarded stimulus is switched to a specific shape (triangle), regardless of color. ITI inter-trial interval, + rewarded stimulus, − unrewarded stimulus