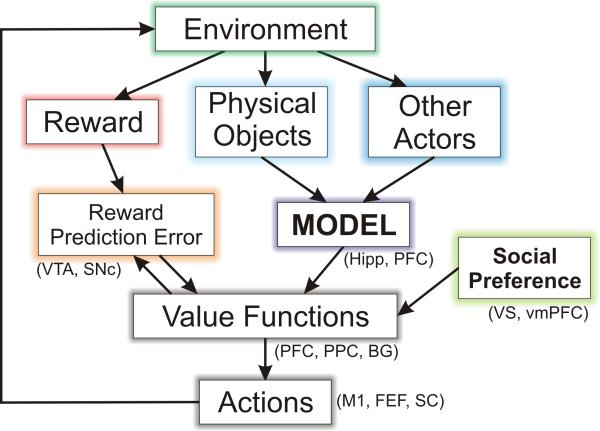
Figure 1.
Components of social decision making and their possible neural substrates. The environment of a decision maker provides 3 different types of information useful for decision making. First, it delivers reward, and its deviation from the predicted reward (reward prediction error) modifies the value functions used to select actions. Second, information about various physical objects can be used to update the decision maker's model about his or her environment. Third, observed actions of other actors can be used to update the decision maker's model about their likely future behaviors. In addition, social preference of the decision makers can also influence their value functions. FEF, frontal eye field; Hipp, hippocampus; M1, primary motor cortex; PFC, prefrontal cortex; PPC, posterior parietal cortex; SC, superior colliculus; SNc, substantia nigra pars compacta; vmPFC, ventromedial prefrontal cortex; VS, ventral striatum; VTA, ventral tegmental area.