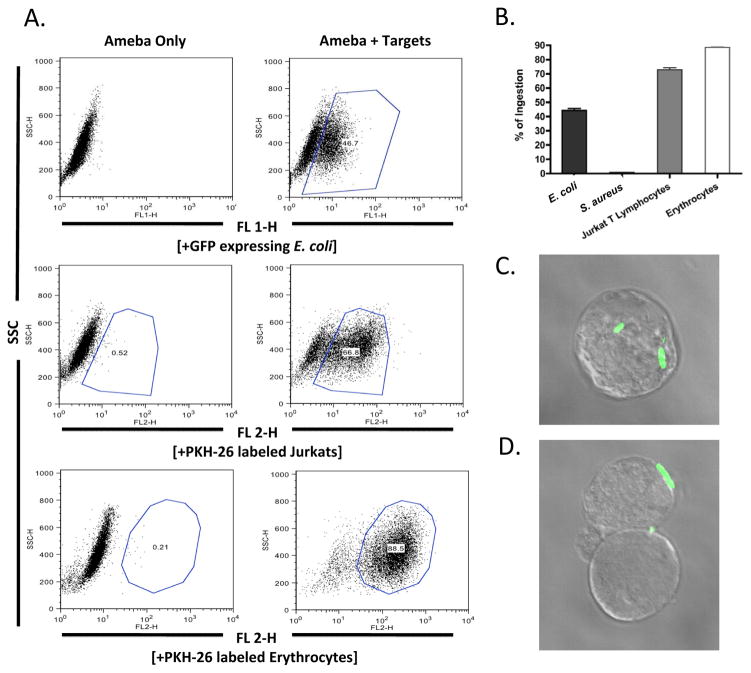
Fig. 2.
Flow cytometry analysis of bacterial ingestion by Entamoeba histolytica. Trophozoites of E. histolytica were incubated with various targets, washed with D-galactose to remove bound but not ingested targets, fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde and analyzed by flow cytometry (A). Trophozoites readily ingested Escherichia coli bacteria, human erythrocytes, and Jurkat T lymphoycytes but not Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (B). Fluorescence microscopy was utilized to visualize the ingestion (C) and adherence (D) of GFP expressing E. coli bacteria. Data is represented as the Mean Fluorescence Intensity percentage of trophozoites ingesting targets. Error bars shown represent the S.E.M. SSC, Side Scatter.