Figure 3.
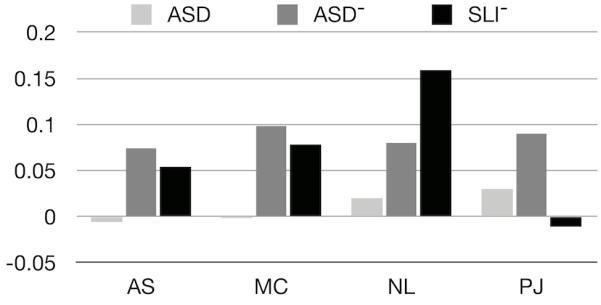
Changes in supralinguistic measure heritability relative to a control condition, where unaffected individuals were randomly removed form the analysis using the same statistical procedure as for ASD and SLI subjects. Our baseline analysis, ASD (all subjects), is equivalent to randomly removing individuals from the analysis as shown by the slight deviations from the control baseline (lightest gray). Both ASD− and SLI− show large deviations on the supralinguistic measures relative to the control condition. ASD− and SLI− induce similar changes in heritability for both AS (ambiguous sentences) and MC (meaning from context) while NL (non-literal language) also shows changes in heritability but SLI− is greater than ASD−. A notable difference is in PJ (pragmatic judgment) where SLI− is consistent with the control condition (i.e., no effect of SLI on PJ heritability).
