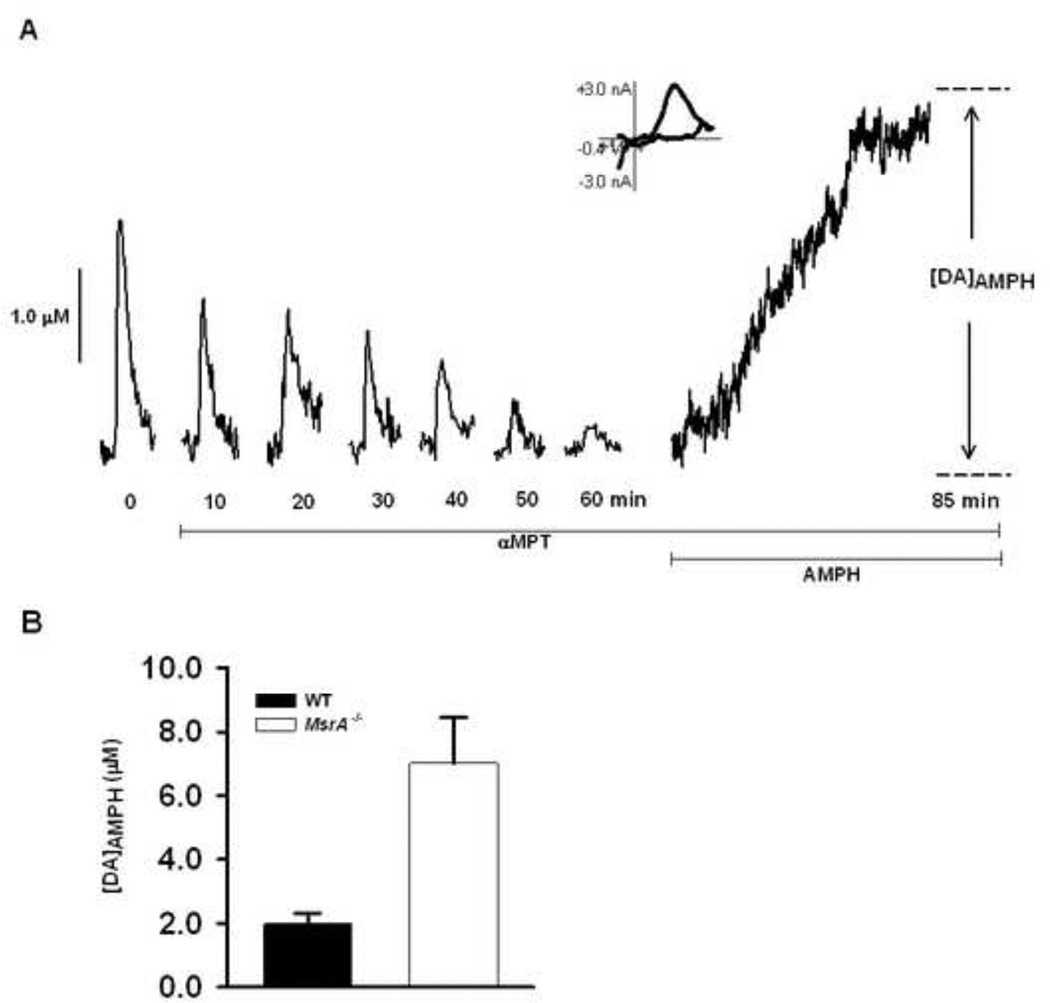
Figure 1. AMPH induced DA efflux is increased in MsrA−/− mice compared to WT mice.
(A) Representative data in which a brain slice from a WT mouse was treated with 50 µM aMPT while single stimulus pulses were applied every 5 min until DA release was diminished. The slice was then treated with 20 µM AMPH for 25 min, and DA]AMPH was measured. A CV is provided from the time of peak release, and confirms the release of DA. (B) In MsrA−/− mice, [DA]AMPH is significantly higher in MsrA−/− slices than in WT slices (*p < 0.05; MsrA−/−, 7.02 ± 1.42 µM, n = 5 mice; WT, 5.63 ± 0.33 µM, n = 4).