Figure 1.
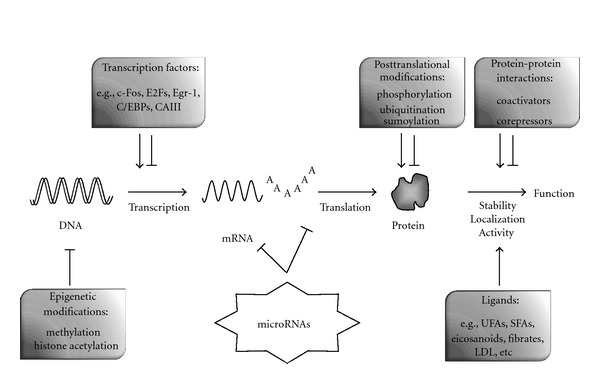
Regulation of PPARs expression and activity. The scheme presents distinct mechanisms reported to regulate the expression and activity of specific PPARs isoforms. Epigenetic mechanisms, including DNA methylation and histone acetylation, may restrict the PPARs promoter activity and several transcription factors have been described to modulate either positively or negatively the transcription of distinct PPARs. As well, posttranslational modifications at the protein level (phosphorylation, ubiquitination, and sumoylation) and interactions with coactivators (e.g., CBP/p300, SRC-1, PGC1α) or corepressors (e.g., RIP-140α, SMRT α) regulate the transcriptional activity, localization, and stability of PPARs isoforms. miRNAs represent a new recently described class of regulators of PPARs transcriptional activity by exerting a control on PPARs mRNA degradation and translation.
