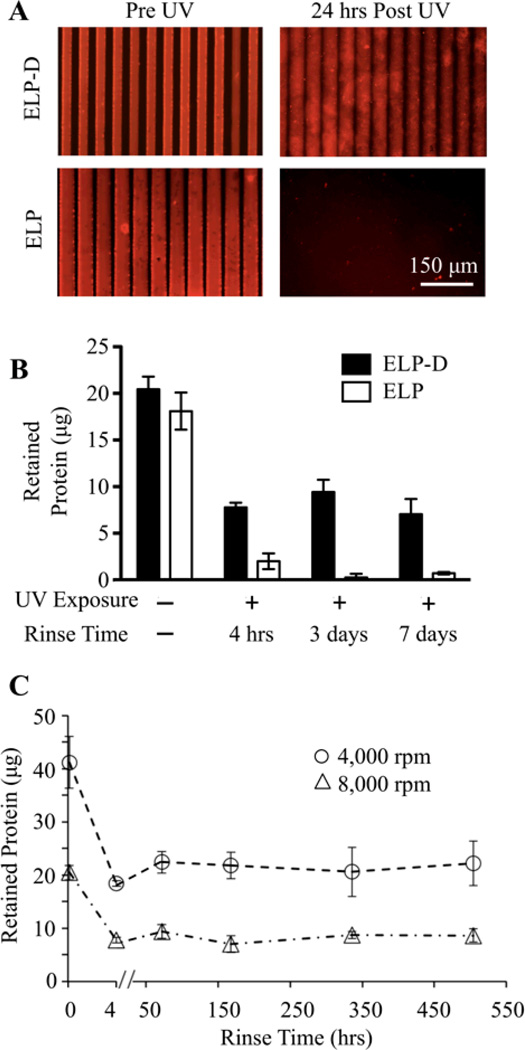
Fig.3.
Photocrosslinked ELP-D stability. (A) Fluorescent images of ELP-D (top) and ELP (bottom) scaffolds micropatterned by soft lithography to have a repetitive striped topography (50 µm wide, 5 µm depth pattern). Dried scaffolds prior to UV light exposure clearly shows the presence of topography (left), while 24 hours after UV exposure and rinsing, only the hydrated ELP-D scaffold remains. (B) Mass of protein retained in spin coated thin films prior to UV exposure and at various times post exposure (in solution), for ELP and ELP-D samples. (C) Long-term, hydrated stability of spin coated ELP-D thin films processed to have different initial masses.