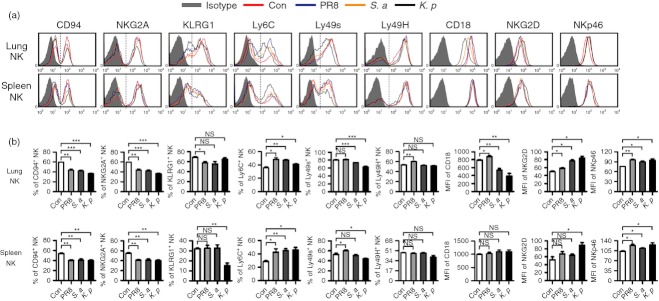
Figure 8.
Increased natural killer (NK) cell function after respiratory infection. C57BL/6 mice were infected intranasally with 0·1 haemagglutination units of influenza A virus (PR8 strain), 1 × 107 colony-forming units (CFU) of Staphylococcus aureus (S. a) or 1 × 107 CFU of Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. p), respectively. Mice were killed, and lymphocytes were isolated from lung and spleen at day 2 post-infection. (a) Flow cytometry assay determined the expression of CD94, NKG2A, KLRG1, Ly6C, Ly49s, Ly49H, CD18, NKG2D and NKp46 on NK cells (CD3− NK1.1+). Histograms are representative of three independent experiments using three mice per group, the shadow histogram is isotype control. (b) The frequencies or the mean fluorescence intensity values are shown as mean ± SEM. *P < 0·05; **P < 0·01; ***P < 0·001; NS, not significant.