Figure 9.
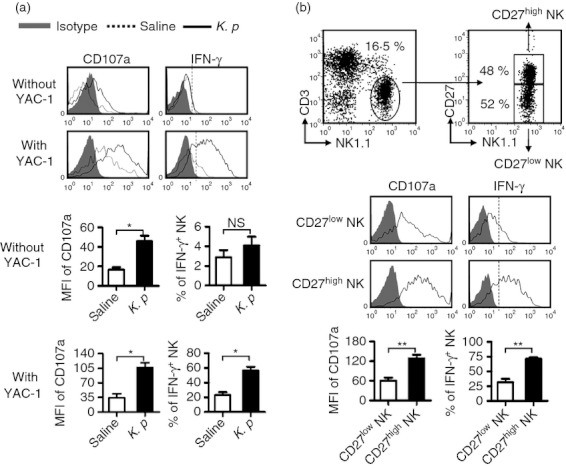
Lung natural killer (NK) cells gain functions rapidly after respiratory infection. C57BL/6 mice were infected intranasally with 1 × 107 colony-forming units (CFU) of K. pneumoniae. At day 2 post-infection, mice were killed, and lymphocytes were isolated from lung and stimulated for 4 hr with YAC-1 cells or not in presence of monensin and anti-CD107a antibody, cells were then surface-stained and intracellular interferon-γ (IFN-γ) was revealed. (a) Flow cytometry assay determined the expression of CD107a and production of IFN-γ on NK cells. The frequencies or the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) values are shown as mean ± SEM. (b) The MFI values of CD107a on CD27high and CD27low NK cells and the frequencies of IFN-γ+ NK cells in CD27high and CD27low NK cells are shown as mean ± SEM. Histograms are representative of three independent experiments using three mice per group, the shadow histogram is isotype control. *P < 0·05; **P < 0·01; NS, not significant.
