Figure 5.
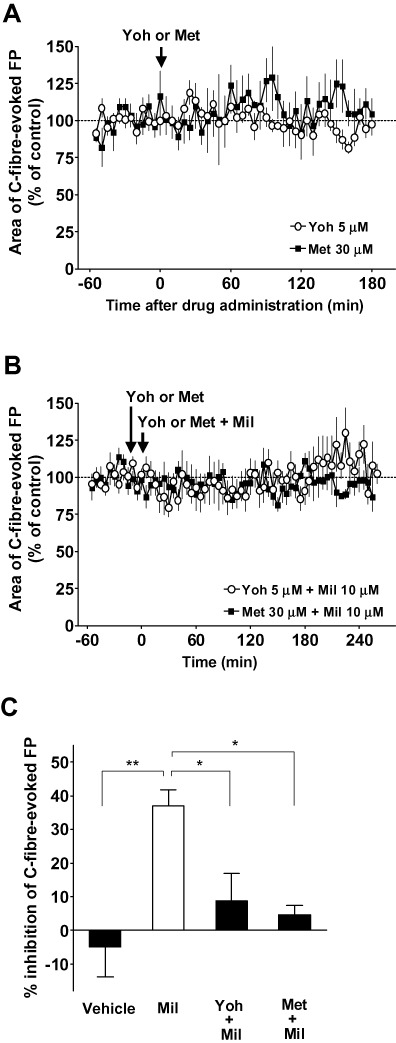
Effects of adrenoceptor or 5-HT receptor antagonists on the inhibitory effect of milnacipran (Mil) on the basal C-fibre-evoked field potentials (FPs) in modified spinal nerve ligation (SNL)-model animals. FPs in the spinal dorsal horn were elicited by electrical stimulation of the sciatic nerve fibres at 1 min intervals in modified SNL-model animals. Five consecutive responses were averaged. (A) Yohimbine (Yoh; n= 4) or methysergide (Met; n= 4) was administered spinally (arrow) after ≥60 min of stable baseline recordings. Each area of C-fibre-evoked FPs was normalized to the mean of 60 consecutive responses obtained prior to the administration (–60 to 0 min in the graph). (B) Yohimbine (n= 4) or methysergide (n= 4) was administered spinally after ≥45 min of stable baseline recordings (time at −15 min in the graph). Yohimbine or methysergide plus milnacipran were administered spinally 15 min after the administration of yohimbine or methysergide alone (time at 0 min in the graph). Each area of C-fibre-evoked FPs was normalized to the mean of 60 consecutive responses obtained prior to the administration of milnacipran (−60 to 0 min in the graph). (C) The inhibitory effects of 10 µM milnacipran on the basal C-fibre-evoked FPs with or without yohimbine or methysergide in modified SNL-model animals. The % inhibition of C-fibre-evoked FPs was calculated using the mean area of 30 consecutive FPs during 90–120 min following the vehicle or milnacipran administration in comparison to the baseline (averaged at −60 to 0 min in B or Figure 4). The values in vehicle and milnacipran groups are from Figure 4. Data shown are means ± SEM. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01, significantly different as indicated.
