Figure 5.
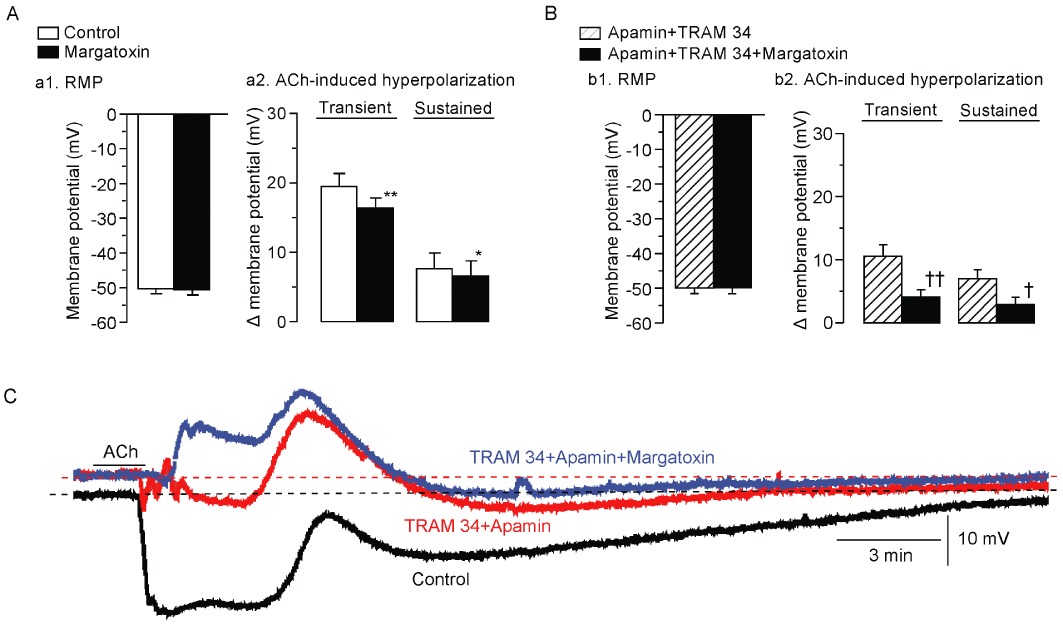
Effects of margatoxin on ACh-induced hyperpolarization in the absence and presence of TRAM 34 plus apamin. (A) Effect of margatoxin (0.3 µM) on resting SMC membrane potential (RMP, a1) and ACh (3 µM)-induced hyperpolarization in the presence of l -NNA + diclofenac (a2). Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n= 5–8). (B). Effect of margatoxin on resting SMC membrane potential (b1) and ACh-induced hyperpolarization (b2) in the presence of l -NNA + diclofenac + apamin + TRAM 34. Data are shown as mean ± SEM (n= 4). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. ‘Control’. †P < 0.05, ††P < 0.01 vs. ‘Apamin + TRAM 34’. (C). Actual tracings showing the effect of margatoxin on ACh-induced hyperpolarization. After the control ACh (3 µM) response had been recorded (‘Control’), apamin plus TRAM 34 were applied as a pretreatment for 5 min and ACh was applied again (‘Apamin + TRAM 34’). Following a 30 min washout with Krebs solution containing l -NNA + diclofenac, apamin + TRAM 34 + margatoxin were applied as a pretreatment for 5 min and ACh was applied the final time (‘Apamin + TRAM 34 + Margatoxin’).
