Abstract
Murine monoclonal antibodies to human cytomegalovirus (CMV) strain AD169 were selected that neutralized virus infectivity. One monoclonal antibody-producing hybridoma, 1G6, was used to produce ascites fluid from which immunoglobulin was isolated. This antibody efficiently neutralized CMV AD169, other laboratory strains (Towne, Davis), and clinical isolates of CMV in early tissue culture passage (less than 10) in the absence of complement. The antibody immunoprecipitated a single 86,000-dalton protein from both laboratory and clinical strains. This viral protein was demonstrated by indirect immunofluorescence to be localized in the cytoplasm of CMV-infected cells.
Full text
PDF

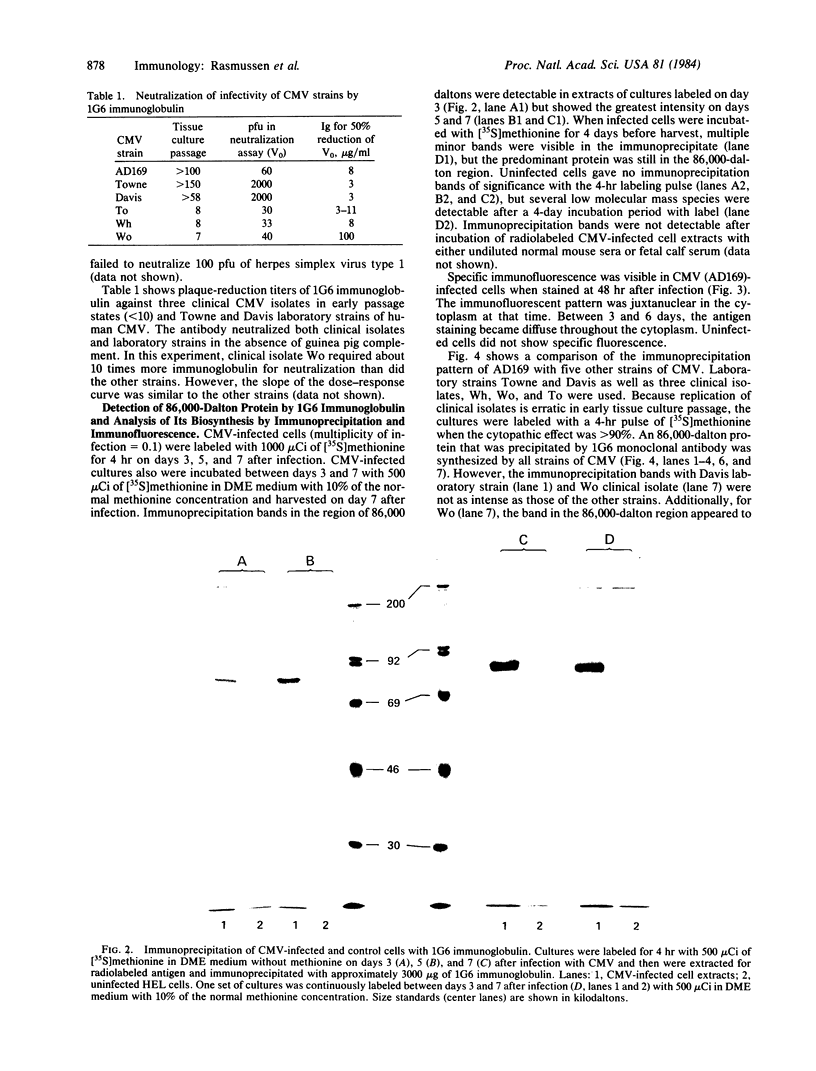


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashe W. K., Notkins A. L. Neutralization of an infectious herpes simplex virus-antibody complex by anti-gamma-globulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):447–451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanas A. C., Gould E. A., Clegg J. C., Varma M. G. Monoclonal antibodies to Sindbis virus glycoprotein E1 can neutralize, enhance infectivity, and independently inhibit haemagglutination or haemolysis. J Gen Virol. 1982 Jan;58(Pt 1):37–46. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-58-1-37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Long D., Pereira L., Hampar B., Zweig M., Cohen G. H. Effect of monoclonal antibodies on limited proteolysis of native glycoprotein gD of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):478–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.478-488.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Ponce de Leon M., Cohen G. H. Comparative structural analysis of glycoprotein gD of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):428–435. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.428-435.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiala M., Honess R. W., Heiner D. C., Heine J. W., Jr, Murnane J., Wallace R., Guze L. B. Cytomegalovirus proteins. I. Polypeptides of virions and dense bodies. J Virol. 1976 Jul;19(1):243–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.1.243-254.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flamand A., Wiktor T. J., Koprowski H. Use of hybridoma monoclonal antibodies in the detection of antigenic differences between rabies and rabies-related virus proteins. II. The glycoprotein. J Gen Virol. 1980 May;48(1):105–109. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-48-1-105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Structural and nonstructural proteins of strain Colburn cytomegalovirus. Virology. 1981 Jun;111(2):516–537. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90354-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer J. P., Friedman H. M., Grossman R. A., Starr S. E., Barker C. F., Perloff L. J., Huang E. S., Plotkin S. A. Live cytomegalovirus vaccination of renal transplant candidates. A preliminary trial. Ann Intern Med. 1979 Nov;91(5):676–683. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-91-5-676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. C., McDougall J., Hackman R., Meyers J. D., Thomas E. D., Nowinski R. C. Monoclonal antibodies to cytomegalovirus: rapid identification of clinical isolates and preliminary use in diagnosis of cytomegalovirus pneumonia. Infect Immun. 1982 Oct;38(1):273–281. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.1.273-281.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham B. J., Minamishima Y., Dresman G. R., Haines H. G., Benyesh-Melnick M. Complement-requiring neutralizing antibodies in hyperimmune sera to human cytomegaloviruses. J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1618–1630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., St Jeor S., Rapp F. Comparison of the polypeptides of several strains of human cytomegalovirus. J Gen Virol. 1977 Mar;34(3):447–454. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-34-3-447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Radbruch A., Liesegang B., Rajewsky K. A new mouse myeloma cell line that has lost immunoglobulin expression but permits the construction of antibody-secreting hybrid cell lines. J Immunol. 1979 Oct;123(4):1548–1550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Sapienza V. J., Carp R. I., Moon H. M. Analysis of structural polypeptides of purified human cytomegalovirus. J Virol. 1976 Dec;20(3):604–611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.3.604-611.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee G. T., Para M. F., Spear P. G. Location of the structural genes for glycoproteins gD and gE and for other polypeptides in the S component of herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):41–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.41-49.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majer M. Virus sensitization. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;58:69–84. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65357-5_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mocarski E. S., Stinski M. F. Persistence of the cytomegalovirus genome in human cells. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):761–775. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.761-775.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B. Immunochemistry of herpes simplex virus glycoproteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1980;90:67–106. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67717-5_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Glycoprotein gE of herpes simplex virus type 1: effects of anti-gE on virion infectivity and on virus-induced fc-binding receptors. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):129–136. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.129-136.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Hoffman M., Cremer N. Electrophoretic analysis of polypeptides immune precipitated from cytomegalovirus-infected cell extracts by human sera. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):933–942. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.933-942.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Hoffman M., Gallo D., Cremer N. Monoclonal antibodies to human cytomegalovirus: three surface membrane proteins with unique immunological and electrophoretic properties specify cross-reactive determinants. Infect Immun. 1982 Jun;36(3):924–932. doi: 10.1128/iai.36.3.924-932.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radwan A. I., Burger D. The role of sensitizing antibody in the neutralization of equine arteritis virus by complement or anti-IgG serum. Virology. 1973 Jun;53(2):366–371. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90215-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen L. E., Jordan G. W., Stevens D. A., Merigan T. C. Lymphocyte interferon production and transformation after Herpes simplex infections in humans. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):728–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen L., Kelsall D., Nelson R., Carney W., Hirsch M., Winston D., Preiksaitis J., Merigan T. C. Virus-specific IgG and IgM antibodies in normal and immunocompromised subjects infected with cytomegalovirus. J Infect Dis. 1982 Feb;145(2):191–199. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.2.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rundell B. B., Betts R. F. Neutralization and sensitization of cytomegalovirus by IgG antibody, anti-IgG antibody, and complement. J Med Virol. 1982;10(2):109–118. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890100205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Abady I. The morphogenesis of human cytomegalovirus. Isolation and polypeptide characterization of cytomegalovirions and dense bodies. Virology. 1975 Aug;66(2):464–473. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90218-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz H., Müller-Lantzsch N., Peteler G. Human immune response to proteins of cytomegalovirus. Intervirology. 1980;13(3):154–161. doi: 10.1159/000149120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinski M. F. Human cytomegalovirus: glycoproteins associated with virions and dense bodies. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):594–609. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.594-609.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Geilinger K. Monoclonal antibodies against the major glycoprotein (gp350/220) of Epstein-Barr virus neutralize infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5307–5311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk W. A., Synder R. M., Benjamin D. C., Wagner R. R. Monoclonal antibodies to the glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus: comparative neutralizing activity. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):220–227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.220-227.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]