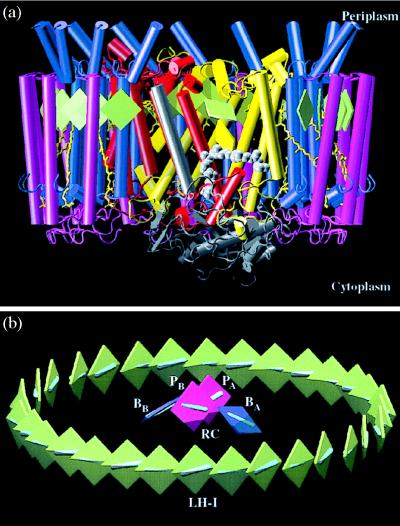
Figure 4.
Structure of the LH-I–RC complex. (a) Side view of the LH-I–RC complex with three LH-I αβ-heterodimers on the front side removed to expose the RC in the interior. The α-helices are represented as cylinders with the L, M, and H subunits of the RC in yellow, red, and gray, and the α-apoprotein and the β-apoprotein of the LH-I in blue and magenta. BChls and bacteriopheophytins are represented as green and yellow squares, respectively. Carotenoids (spheroidenes) are in a yellow licorice representation, and quinone QB is rendered by gray van der Waals spheres. QB shuttles in and out (as QBH2) of the LH-I–RC complex as indicated in Fig. 1. (b) Arrangement of BChls in the LH-I–RC complex. The BChls are represented as squares with B875 BChls of LH-I in green, and the special pair (PA and PB) and the accessory BChls (BA and BB) of the RC in red and blue, respectively; cyan bars represent Qy transition moments of BChls. [Produced with the program vmd (25)].