Abstract
An immunoassay method is described for the quantitative determination of synapsin I (protein I) and of a 36,000-dalton membrane protein from rat brain synaptic vesicles. The samples are spotted on nitrocellulose membrane filters, incubated sequentially with specific antibodies and 125I-labeled protein A, and assayed for radioactivity in a gamma scintillation counter. Conditions have been established to prevent losses of protein from the sheets during processing, to quench background radioactivity, and to adjust the sensitivity to the range desired. A large number of samples can be handled in parallel. The assay does not require iodination of the antigen and is accurate even with crude tissue samples. Standard curves were linear over a 20- to 50-fold range. The sensitivity of the method is such that 10 pmol of synapsin I and 50 ng of total vesicle membrane protein could be measured with accuracy. The method should prove useful for a wide range of proteins.
Full text
PDF
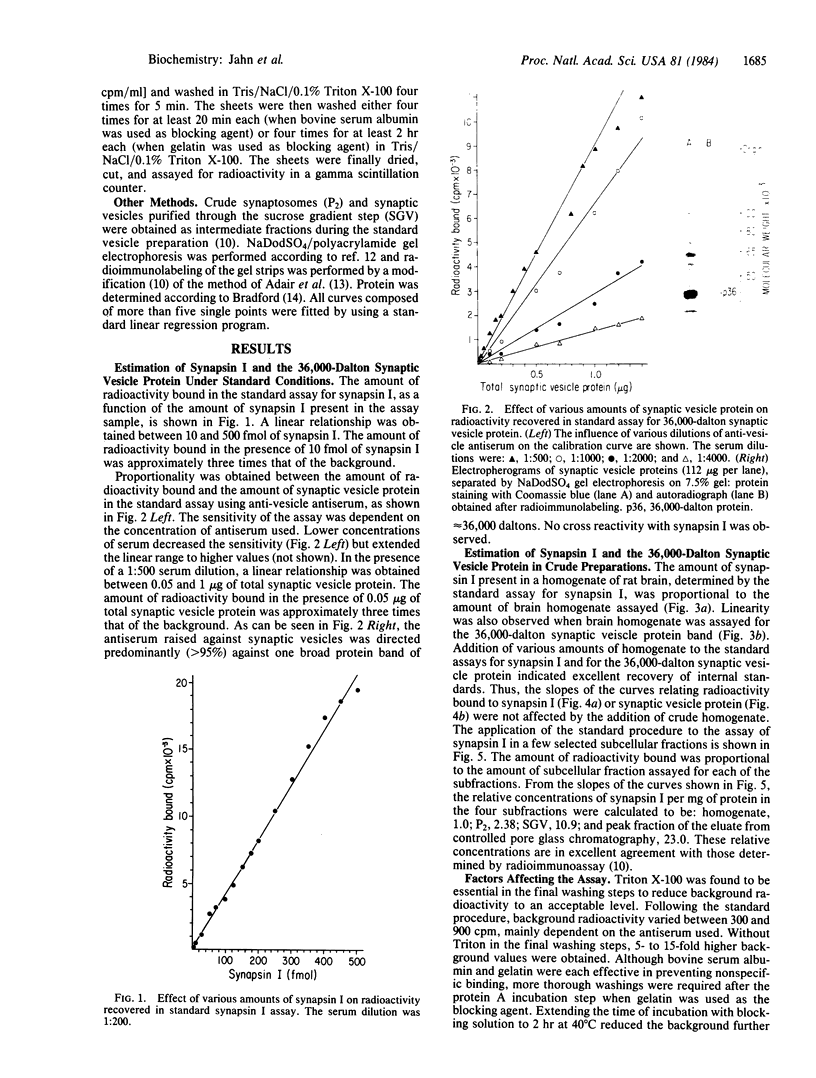
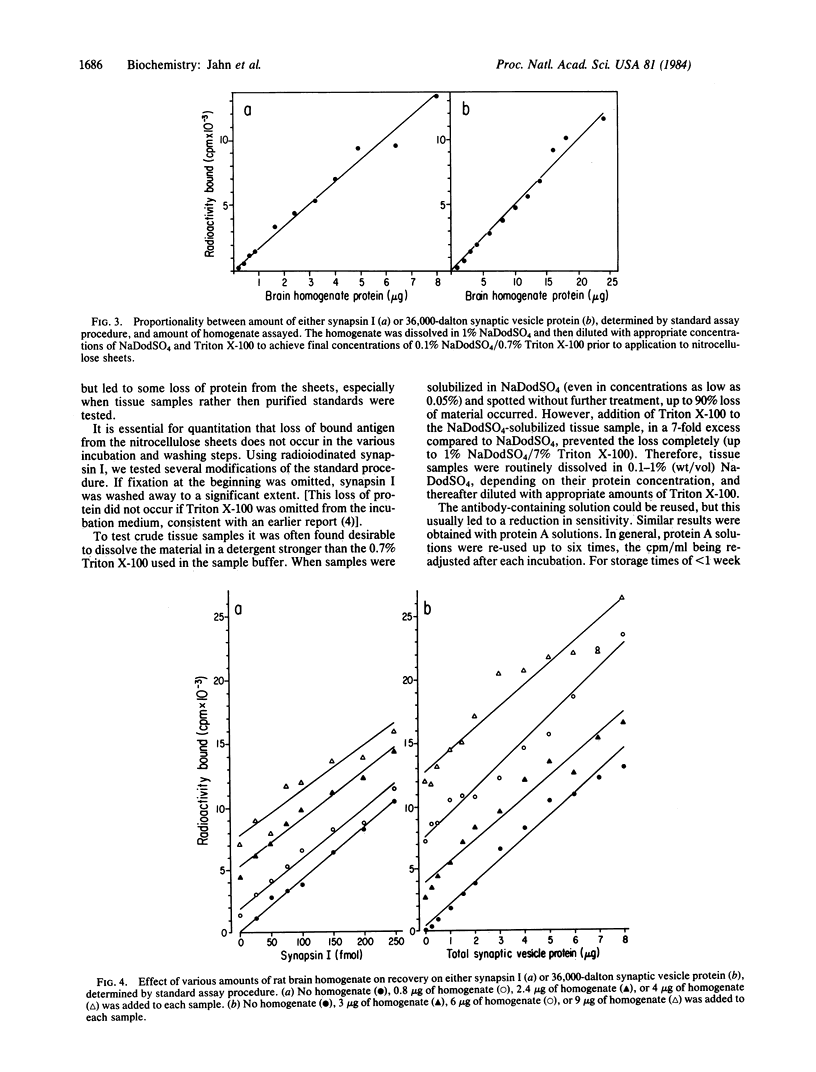
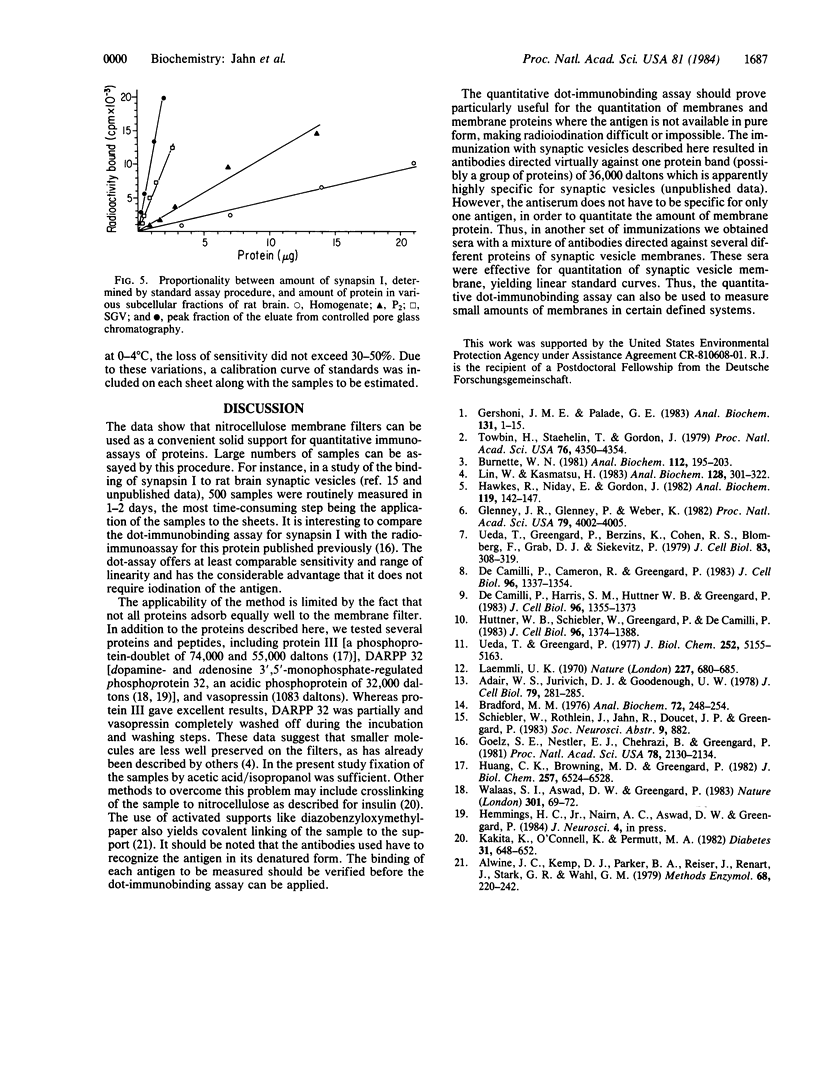
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adair W. S., Jurivich D., Goodenough U. W. Localization of cellular antigens in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. J Cell Biol. 1978 Oct;79(1):281–285. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.1.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Parker B. A., Reiser J., Renart J., Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Detection of specific RNAs or specific fragments of DNA by fractionation in gels and transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:220–242. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68017-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Cameron R., Greengard P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. I. Its general distribution in synapses of the central and peripheral nervous system demonstrated by immunofluorescence in frozen and plastic sections. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1337–1354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Camilli P., Harris S. M., Jr, Huttner W. B., Greengard P. Synapsin I (Protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. II. Its specific association with synaptic vesicles demonstrated by immunocytochemistry in agarose-embedded synaptosomes. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1355–1373. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershoni J. M., Palade G. E. Protein blotting: principles and applications. Anal Biochem. 1983 May;131(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90128-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenney J. R., Jr, Glenney P., Weber K. Erythroid spectrin, brain fodrin, and intestinal brush border proteins (TW-260/240) are related molecules containing a common calmodulin-binding subunit bound to a variant cell type-specific subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4002–4005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelz S. E., Nestler E. J., Chehrazi B., Greengard P. Distribution of protein I in mammalian brain as determined by a detergent-based radioimmunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2130–2134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C. K., Browning M. D., Greengard P. Purification and characterization of protein IIIb, a mammalian brain phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6524–6528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huttner W. B., Schiebler W., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Synapsin I (protein I), a nerve terminal-specific phosphoprotein. III. Its association with synaptic vesicles studied in a highly purified synaptic vesicle preparation. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1374–1388. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakita K., O'Connell K., Permutt M. A. Immunodetection of insulin after transfer from gels to nitrocellulose filters. A method of analysis in tissue extracts. Diabetes. 1982 Jul;31(7):648–652. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.7.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein system of neuronal membranes. I. Solubilization, purification, and some properties of an endogenous phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5155–5163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Greengard P., Berzins K., Cohen R. S., Blomberg F., Grab D. J., Siekevitz P. Subcellular distribution in cerebral cortex of two proteins phosphorylated by a cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J Cell Biol. 1979 Nov;83(2 Pt 1):308–319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.2.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walaas S. I., Aswad D. W., Greengard P. A dopamine- and cyclic AMP-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):69–71. doi: 10.1038/301069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]