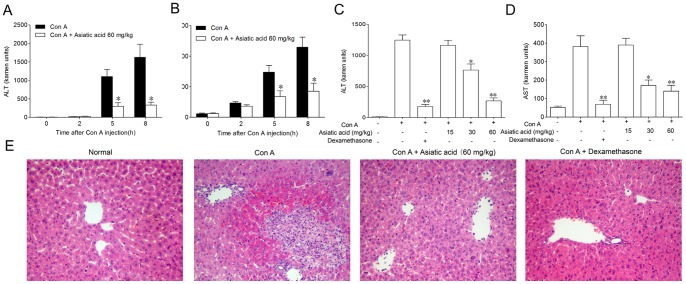
Figure 5. Asiatic acid protects against Con A-induced T-cell-mediated acute fulminant hepatitis in mice. BALB/c mice were received an intravenous Con A injection (15 mg/kg body weight).
In the drug treatment group, asiatic acid (intragastric administration) and dexamethason (intramscular injection) were given twice at 8 h before and 1 h after Con A injection, respectively. (A, B) Time course of serum alanine transaminase (ALT) and aspartate transaminase (AST) release. Values are shown as the means ± SEM of three mice at each time point. *P<0.05 vs. Con A group at the same time point. (C, D) Dose-dependent inhibition on ALT and AST release. Values are shown as the means ± SEM of eight mice in each group. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. Con A group. (E) Photomicrographs of representative mouse livers with H&E staining are shown (original magnification ×100).