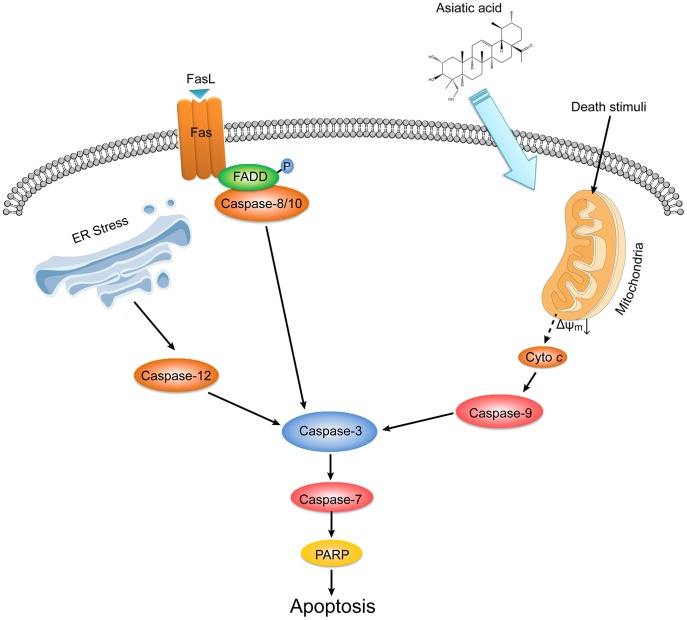
Figure 8. Overview of cell death pathways for asiatic acid-induced apoptosis in Con A-activated T cells.
Asiatic acid triggered apoptosis of Con A-activated T cells in a mitochondria-dependent manner indicated by the disruption of the mitochondrial transmembrane potential, release of cytochrome c from mitochondria to cytosol, caspase-9 and caspase-3 activation and cleavage of PARP. At the same time, following activation of T cells from MRLlpr/lpr mice with mutation of Fas demonstrated a similar susceptibility to asiatic acid-induced apoptosis compared with normal T cells. In addition, asiatic acid hardly influenced caspase-12 activation and the expression of GRP78 and CHOP. Taken together, these results suggest that Fas-mediated death-receptor apoptotic pathway and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-mediated apoptotic pathway do not mainly contribute to asiatic acid-induced cell death.