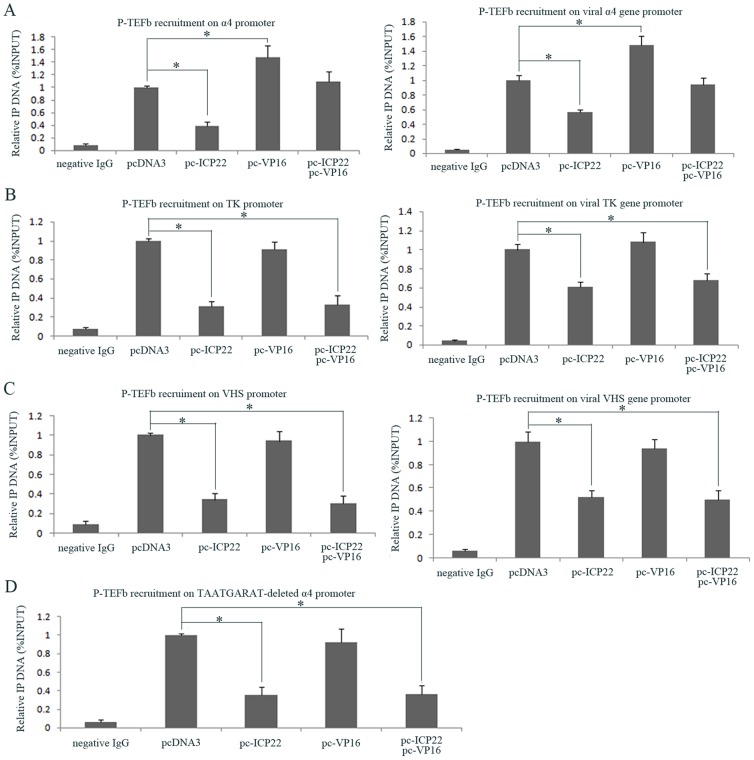
Figure 5. The effects of P-TEFb recruitment on viral α-, β- and γ-gene promoters in the presence of VP16 and ICP22.
(A) The effects of VP16 and ICP22 on the recruitment of P-TEFb to viral α4 gene promoter region. CHO-K1 cells were co-transfected with pGL-α4 plasmid containing α4 gene promoter and ICP22, VP16 or control pcDNA3 expression plasmids as indicated for 40 h and subjected to ChIP assays (left panel). Hep-2 cells were transfected with ICP22, VP16 or control pcDNA3 expression plasmids as indicated for 36 h, and then infected with HSV-1 at an MOI of 10. At 3 h post-infection, the cells were subjected to ChIP assays (right panel). (B) The effects of VP16 and ICP22 on the recruitment of P-TEFb to viral TK gene promoter region. CHO-K1 cells were co-transfected with pGL-TK plasmid containing TK gene promoter and ICP22, VP16 or control pcDNA3 expression plasmids as indicated for 40 h and subjected to ChIP assays (left panel). Hep-2 cells were transfected with ICP22, VP16 or control pcDNA3 expression plasmids as indicated for 36 h, and then infected with HSV-1 at an MOI of 2. At 7 h post-infection, the cells were subjected to ChIP assays (right panel). (C) The effects of VP16 and ICP22 on the recruitment of P-TEFb to viral VHS gene promoter region. CHO-K1 cells were co-transfected with pGL-TK plasmid contained VHS gene promoter and ICP22, VP16 or control pcDNA3 expression plasmids as indicated for 40 h and subjected to ChIP assays (left panel). Hep-2 cells were transfected with ICP22, VP16 or control pcDNA3 expression plasmids as indicated for 36 h, and then infected with HSV-1 at an MOI of 2. At 13 h post-infection, the cells were subjected to ChIP assays (right panel). (D) The effects of VP16 and ICP22 on the recruitment of P-TEFb to the TAATGARAT-deleted α4 promoter. CHO-K1 cells were co-transfected with pGL-α4-Δ16 plasmid containing TAATGARAT-deleted α4-gene promoter and ICP22, VP16 or control pcNDA3 expression plasmids as indicated for 40 h and subjected to ChIP assays. Antibodies specific for CyclinT1 or control rabbit IgG were used for immunoprecipitation. The precipitated DNA was analyzed by RT-PCR using primers specific for the promoter regions of α4, TK, VHS and TAATGARAT-deleted α4. The values are expressed as the percentage of immunoprecipitated input DNA relative to the control group transfected with pcDNA3. Error bars represent the standard deviation from triplicate samples. * P<0.05 by student's t-test.