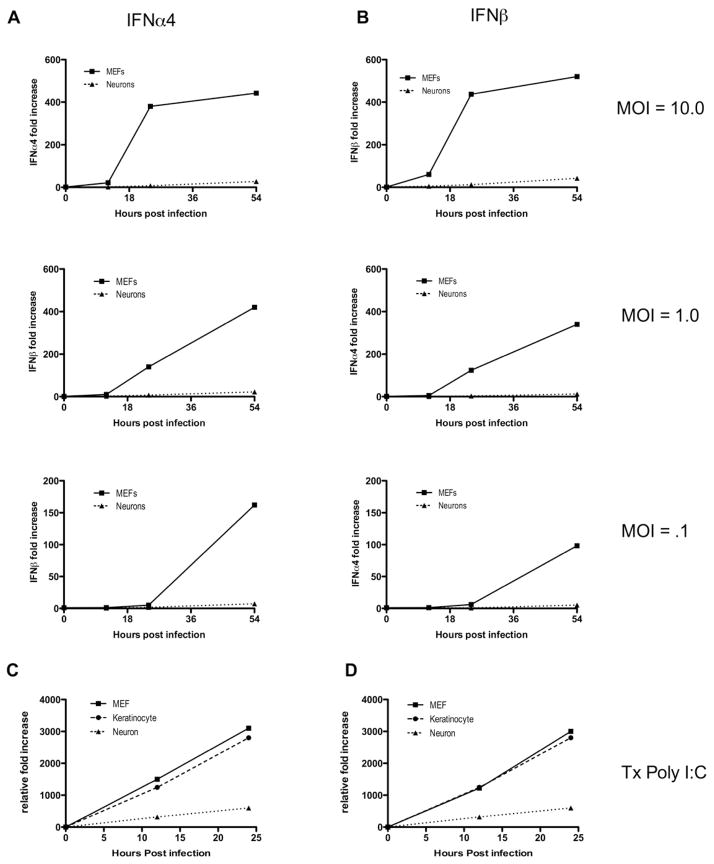
Figure 1. Neurons are impaired in their capacity to respond to viral stimulation and induce type I IFNs.
(A, B) Mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and neurons were infected with HSV1-GFP at MOIs of 0.1, 1.0 and 10.0. RNA was isolated from all cells at 0, 12, 24, and 54 hours post-infection. Relative fold increases in IFN-α4 (A) and IFN-β (B) production were determined by quantitative RT-PCR of isolated RNA relative to the housekeeping gene hprt. (C, D) MEFs, keratinocytes, and neurons were transfected with Poly I:C (1.0 μg/mL). RNA was isolated from all cells at the time points indicated, and fold increases of IFN-α4 (C) and IFN-β (D) relative to hprt were determined by RT-qPCR. Data are representative of three independent experiments. See also Figure S1.