Fig. 3.
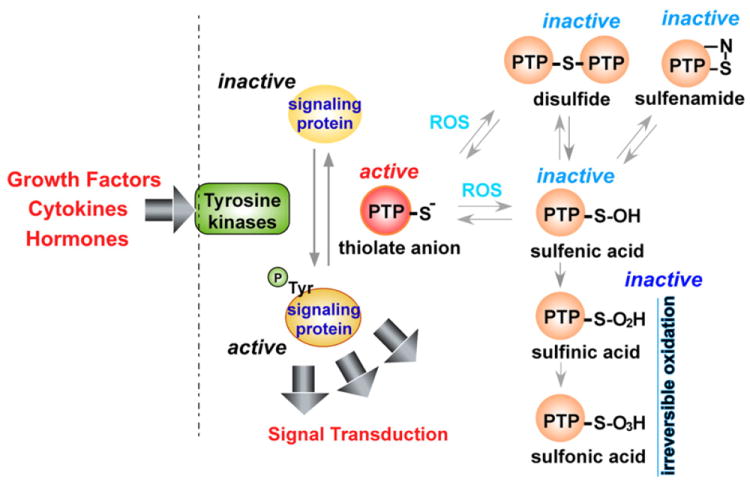
Mechanism of ROS-mediated protein tyrosine phosphatase inactivation. Tyrosine kinases, activated by growth factors, cytokines, and hormones, phosphorylate target proteins. Phosphorylation can be reversed by protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTP); ROS inactivates PTP by oxidation of catalytic cysteine residues resulting in the formation of the sulfenic acid (−SOH) intermediate that can form disulfide bonds or sulfenamide residues. Further oxidation of sulfenic acid results in formation of sulfinic (−SO2H) or sulfonic acid (−SO3H), which are relatively irreversible.
