Fig. 5.
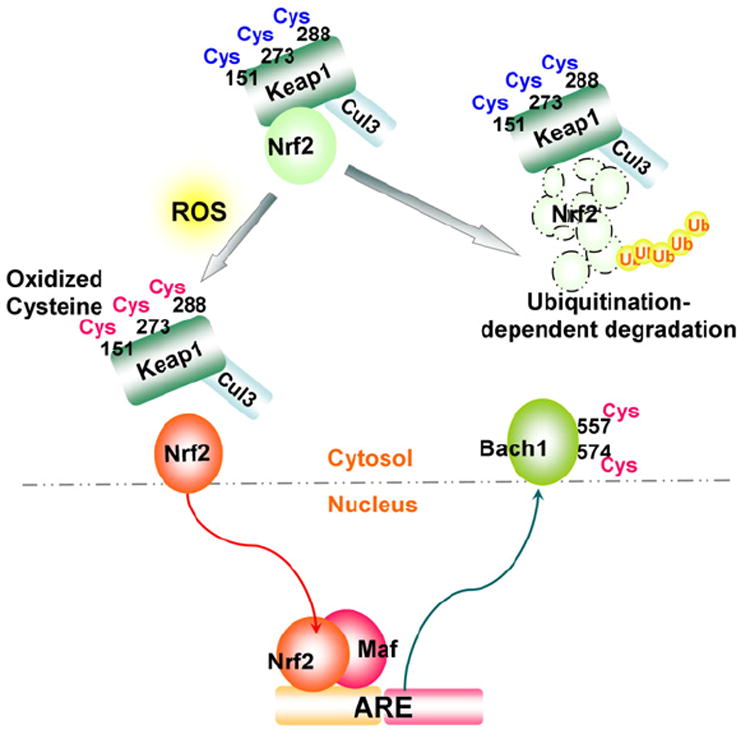
Redox regulation of the Nrf2–ARE pathway. ROS oxidation of cysteines (Cys-151, -273 and -288) in the mouse Kelch-like ECH-associated protein-1 (Keap1) results in the release of Nrf2 from the Keap1/cullin-3 E3-ubiquitin ligase (Cul3) complex, preventing Nrf2 degradation. Nrf2 subsequently undergoes nuclear translocation. In the nucleus, a heterodimer of Nrf2 and small Maf members (Maf-F, Maf-G, and Maf-K) binds the antioxidant-responsive element (ARE); oxidation of a b-zip transcriptional repressor of ARE, the human BTB and CNC homolog 1 (Bach1) at Cys-557 and -574 results in cytoplasmic translocation of Bach1, both leading to activation of the ARE.
