Abstract
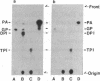
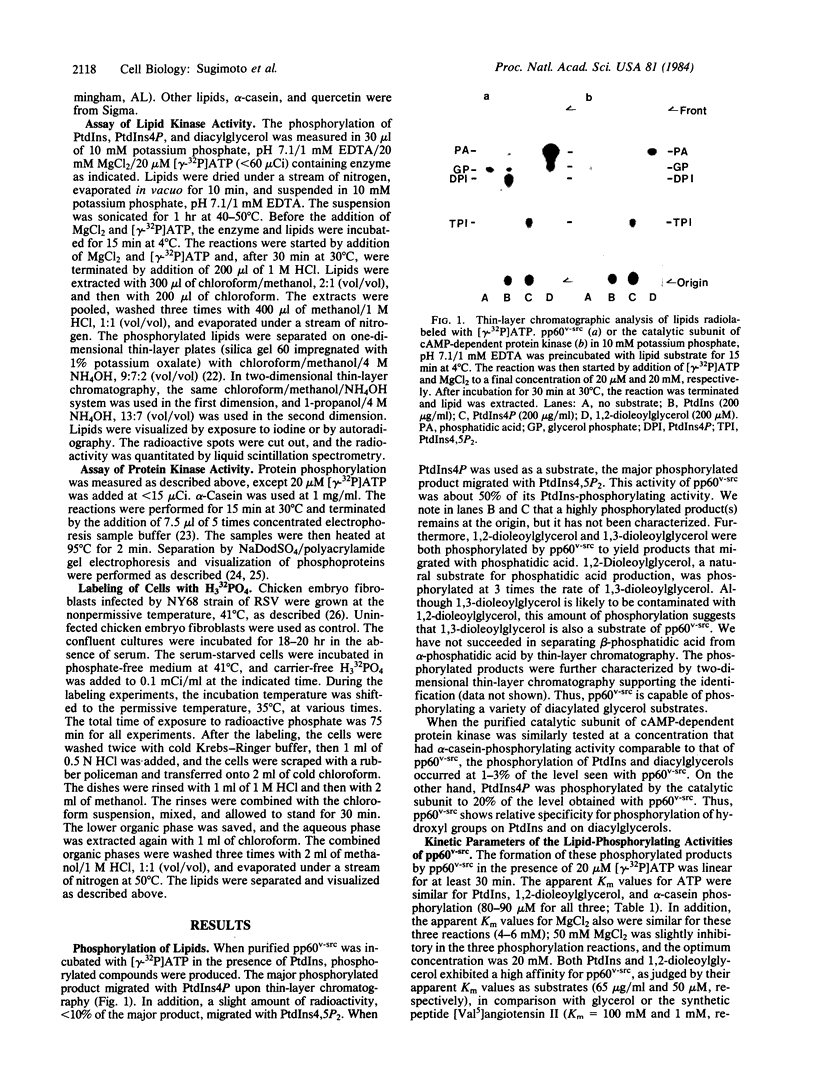
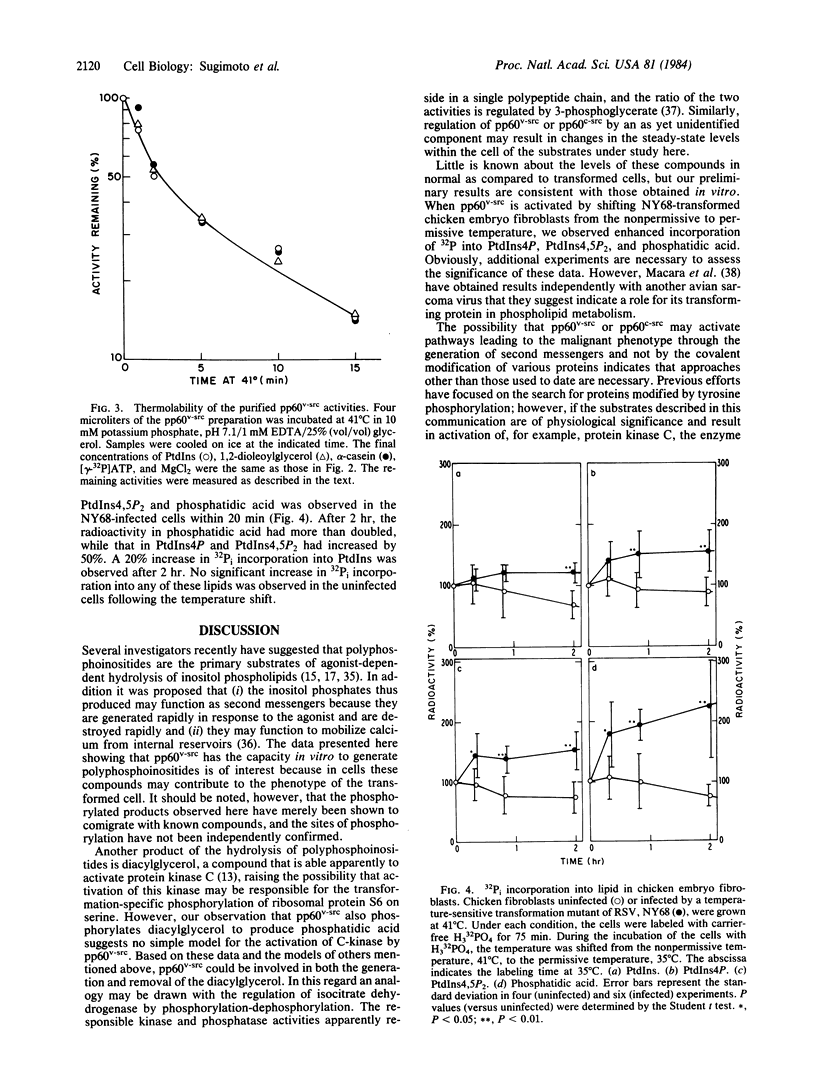
The ability of purified Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product, pp60v-src, to phosphorylate phosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerol was investigated. Phosphatidylinositol was phosphorylated to form both mono- and diphosphorylated derivatives. 1,2-Diacylglycerol was phosphorylated to form phosphatidic acid. These activities showed the same thermolability and the same sensitivity to inhibitors as shown by the casein kinase activity of pp60v-src. In addition, when serum-starved chicken embryo fibroblasts transformed by a virus mutant temperature-sensitive for transformation were shifted from the nonpermissive to permissive temperature, an increase of 50-100% in the labeling of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate, phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate, and phosphatidic acid was observed, as compared to uninfected cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agranoff B. W., Murthy P., Seguin E. B. Thrombin-induced phosphodiesteratic cleavage of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2076–2078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beavo J. A., Bechtel P. J., Krebs E. G. Preparation of homogeneous cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase(s) and its subunits from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1974;38:299–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)38046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Rapid accumulation of inositol trisphosphate reveals that agonists hydrolyse polyphosphoinositides instead of phosphatidylinositol. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):849–858. doi: 10.1042/bj2120849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Reiss N. A., Schwartz R. J., Hunter T. Three glycolytic enzymes are phosphorylated at tyrosine in cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1983 Mar 17;302(5905):218–223. doi: 10.1038/302218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Levinson A. D., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus (pp60src) and a homologous protein in normal cells (pp60proto-src) are associated with the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3783–3787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 in avian sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4112–4115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Friis R. R. Changes in phosphatidylinositol metabolism correlated to growth state of normal and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed Japanese quail cells. Cancer Res. 1977 Sep;37(9):2979–2984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of a cellular protein substrate phosphorylated by the avian sarcoma virus-transforming gene product. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. I., Collett M. S., Erikson E., Purchio A. F., Brugge J. S. Protein phosphorylation mediated by partially purified avian sarcoma virus transforming-gene product. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):907–917. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Sastre F., Folch-Pi J. Thin-layer chromatography of the phosphoinositides. J Lipid Res. 1968 Jul;9(4):532–533. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani Y., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Characterization of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6344–6351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani Y., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product is associated with glycerol kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2126–2129. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graziani Y., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. The effect of quercetin on the phosphorylation activity of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 3;135(3):583–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07692.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jergil B., Sundler R. Phosphorylation of phosphatidylinositol in rat liver Golgi. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7968–7973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. A., Walseth T. F. The enzymatic preparation of [alpha-32P]ATP, [alpha-32P]GTP, [32P]cAMP, and [32P]cGMP, and their use in the assay of adenylate and guanylate cyclases and cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:135–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanoh H., Kondoh H., Ono T. Diacylglycerol kinase from pig brain. Purification and phospholipid dependencies. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1767–1774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Hanafusa H. The effects of reciprocal changes in temperature on the transformed state of cells infected with a rous sarcoma virus mutant. Virology. 1971 Nov;46(2):470–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90047-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk C. J., Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Michell R. H. Hormone-stimulated metabolism of inositol lipids and its relationship to hepatic receptor function. Biochem Soc Trans. 1981 Oct;9(5):377–379. doi: 10.1042/bst0090377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krebs E. G., Beavo J. A. Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:923–959. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.004423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Wang E., Goldberg A. R. Evidence that the src gene product of Rous sarcoma virus is membrane associated. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):25–40. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90480-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaPorte D. C., Koshland D. E., Jr Phosphorylation of isocitrate dehydrogenase as a demonstration of enhanced sensitivity in covalent regulation. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):286–290. doi: 10.1038/305286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Evidence that the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus encodes a protein kinase associated with a phosphoprotein. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: effects of src gene expression on the synthesis and phosphorylation of cellular polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5212–5216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richert N. D., Blithe D. L., Pastan I. Properties of the src kinase purified from Rous sarcoma virus-induced rat tumors. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7143–7150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittenhouse-Simmons S. Production of diglyceride from phosphatidylinositol in activated human platelets. J Clin Invest. 1979 Apr;63(4):580–587. doi: 10.1172/JCI109339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R. Immunofluorescence on avian sarcoma virus-transformed cells: localization of the src gene product. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Beemon K., Eckhart W. Evidence that the phosphorylation of tyrosine is essential for cellular transformation by Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):807–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90327-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streb H., Irvine R. F., Berridge M. J., Schulz I. Release of Ca2+ from a nonmitochondrial intracellular store in pancreatic acinar cells by inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate. Nature. 1983 Nov 3;306(5938):67–69. doi: 10.1038/306067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Iwasa Y., Kawahara Y., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-dependent activation of a multifunctional protein kinase by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3692–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Jay G., Pastan I. Localization of the ASV src gene product to the plasma membrane of transformed cells by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90361-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong T. W., Goldberg A. R. In vitro phosphorylation of angiotensin analogs by tyrosyl protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1022–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]