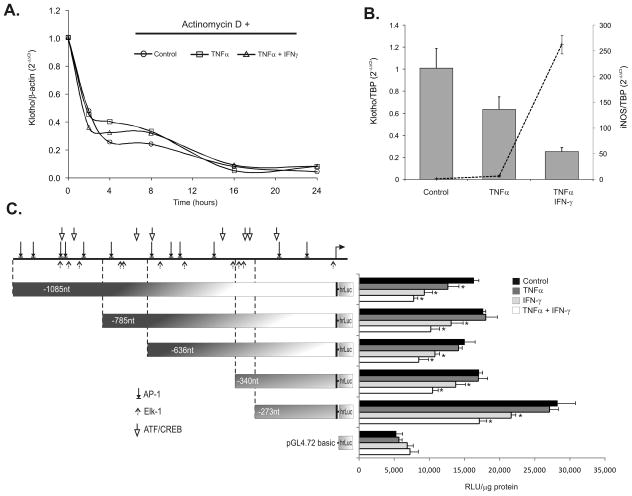
Figure 8. Klotho is regulated by TNF and/or IFN-γ via a transcriptional mechanism.
(A) De novo transcription was inhibited in mpkDCT4 cells with Actinomycin D (ActD) and Klotho transcript decay rate was followed over time by real-time RT-PCR analysis. No significant differences were observed in the rate of mRNA degradation in control (open circles), TNF-treated (open squares) or TNF/IFN-γ co-treated cells (open triangles). (B) The effects of the two cytokines on Klotho (bars) and iNOS (line) expression in mIMCD-3 cells mirrors the effects observed in the mpkDCT4 cells. (C) The effects of TNF, IFN-γ, and their combination on murine Klotho gene promoter activity in transiently transfected mIMCD-3 cells. 5′-deletion constructs spanning -1085nt to -273nt upstream of the transcription start site are depicted with predicted binding sites for the three prototypical JNK-regulated transcription factors, AP- 1,Elk-1, and ATF/CREB (* p<0.05 control vs. cytokine treatment, n=4). Transcription start site, mapped by Shiraki-Iida et al.32 is indicated by a right-pointing arrow.