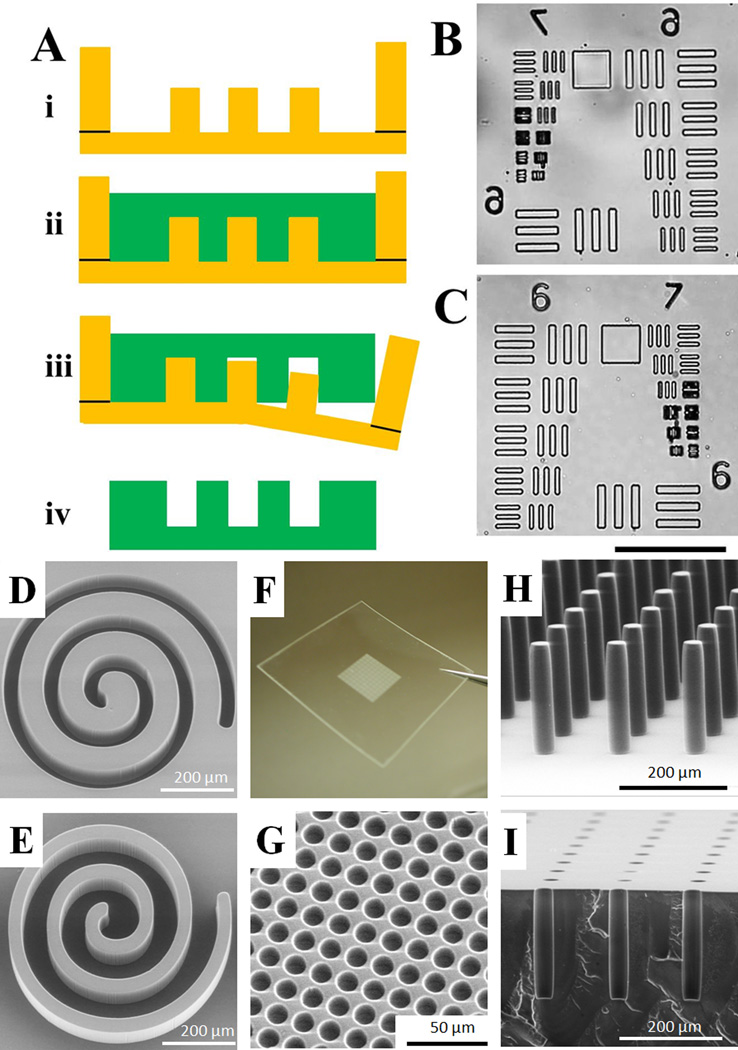
Fig. 1.
Micromolding PS by soft lithography. (A) Schematic of the process. i) A PDMS mold bounded by a raised PDMS well. ii) The PS solution is poured onto the PDMS mold, degassed, and baked to evaporate the GBL solvent. iii) The PDMS mold is released from the solidified PS leaving iv) the micromolded PS part. (B–C) Brightfield microscopy images of the standard USAF 1951 resolution test pattern on the PDMS mold (B) and the replicated PS (C). The scale bar is 100 µm. (D–E) SEM images of a spiral pattern on the PDMS mold (D) and the replicated PS (E). (F–I) A variety of microstructures created in PS by soft lithography. (F) A region of an array possessing 550,000 microwells. (G) SEM image of a section of the array in “F” revealing the individual microwells (12.5 µm diameter, 5 µm inter-well gap, 20 µm depth). (H) Pillars with an aspect ratio >7 (30 µm diameter, 215 µm height). (I) A coronal section of an array composed of microwells with high aspect ratio (30 µm diameter, 215 µm depth).