Abstract
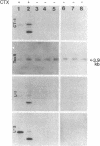
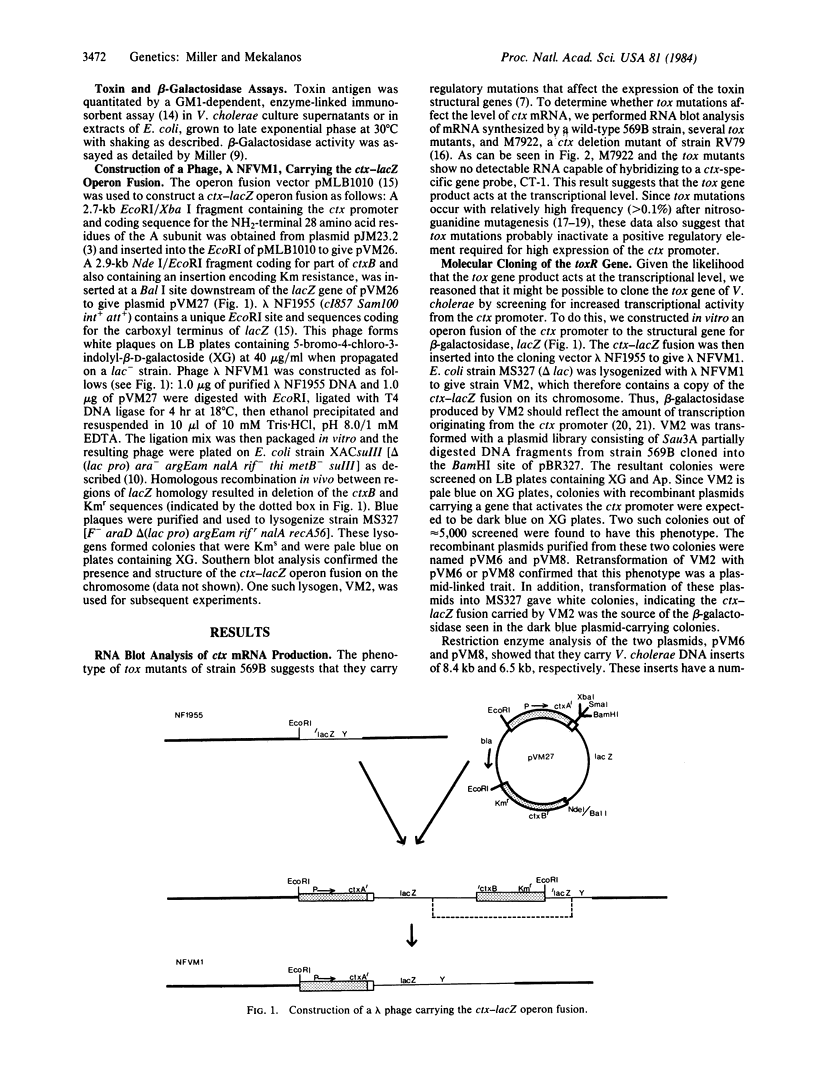
We have cloned a positive regulatory gene ( toxR ) from Vibrio cholerae that controls cholera toxin transcription. This was done by first constructing a genetic fusion consisting of the lacZ gene fused to the promoter of the cholera toxin operon ctxAB . This operon fusion was used to screen a V. cholerae genomic library for genes that could activate the ctx promoter in Escherichia coli. This method allowed the identification of a gene, toxR , that increases ctx expression by more than 100-fold. Complementation analysis indicated that certain hypotoxinogenic mutants of V. cholerae 569B probably have mutations in the toxR gene. Southern blot analysis suggests that all V. cholerae, including nontoxinogenic strains, have the toxR gene. Moreover, nontoxinogenic strains not only lack the structural genes for cholera toxin but also sequences associated with the larger 7-kilobase ctx genetic element.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Adhya S., de Crombrugghe B. Evidence for two functional gal promoters in intact Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11905–11910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baine W. B., Vasil M. L., Holmes R. K. Genetic mapping of mutations in independently isolated nontoxinogenic mutants of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1978 Jul;21(1):194–200. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.1.194-200.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan L. T., 3rd, Ryder R. C., Richardson S. H. Biochemistry of vibrio cholerae virulence. II. Skin permeability factor-cholera enterotoxin production in a chemically defined medium. Infect Immun. 1971 Nov;4(5):611–618. doi: 10.1128/iai.4.5.611-618.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. P. Preparation of the vascular permeability factor of Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):793–795. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.793-795.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallas W. S., Falkow S. Amino acid sequence homology between cholera toxin and Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):499–501. doi: 10.1038/288499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Richardson S. H. In vitro production of choleragen and vascular permeability factor by Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Jul;96(1):126–130. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.1.126-130.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN V. J. Studies on the virulence of bacteriophage-infected strains of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Bacteriol. 1951 Jun;61(6):675–688. doi: 10.1128/jb.61.6.675-688.1951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkelstein R. A., Vasil M. L., Holmes R. K. Studies on toxinogenesis in Vibrio cholerae. I. Isolation of mutants with altered toxinogenicity. J Infect Dis. 1974 Feb;129(2):117–123. doi: 10.1093/infdis/129.2.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Knipe D. M. Mutations in the major DNA-binding protein gene of herpes simplex virus type 1 result in increased levels of viral gene expression. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):478–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.478-486.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg S., Murphy J. R. Molecular epidemiological studies of United States Gulf Coast Vibrio cholerae strains: integration site of mutator vibriophage VcA-3. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):224–230. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.224-230.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes R. K., Vasil M. L., Finkelstein R. A. Studies on toxinogenesis in Vibrio cholerae. III. Characterization of nontoxinogenic mutants in vitro and in experimental animals. J Clin Invest. 1975 Mar;55(3):551–560. doi: 10.1172/JCI107962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren J. Comparison of the tissue receptors for Vibrio cholerae and Escherichia coli enterotoxins by means of gangliosides and natural cholera toxoid. Infect Immun. 1973 Dec;8(6):851–859. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.6.851-859.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanei C., Uchida T., Yoneda M. Isolation from corynebacterium diphtheriae C7(beta) of bacterial mutants that produce toxin in medium with excess iron. Infect Immun. 1977 Oct;18(1):203–209. doi: 10.1128/iai.18.1.203-209.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J. B., Moseley S. L., Falkow S. Molecular characterization of environmental and nontoxigenic strains of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1981 May;32(2):661–667. doi: 10.1128/iai.32.2.661-667.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Collier R. J., Romig W. R. Affinity filters, a new approach to the isolation of tox mutants of Vibrio cholerae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):941–945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Collier R. J., Romig W. R. Simple method for purifying choleragenoid, the natural toxoid of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):789–795. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.789-795.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J. Duplication and amplification of toxin genes in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90228-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Moseley S. L., Murphy J. R., Falkow S. Isolation of enterotoxin structural gene deletion mutations in Vibrio cholerae induced by two mutagenic vibriophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):151–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Murphy J. R. Regulation of cholera toxin production in Vibrio cholerae: genetic analysis of phenotypic instability in hypertoxinogenic mutants. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):570–576. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.570-576.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mekalanos J. J., Swartz D. J., Pearson G. D., Harford N., Groyne F., de Wilde M. Cholera toxin genes: nucleotide sequence, deletion analysis and vaccine development. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):551–557. doi: 10.1038/306551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Michel J. L., Teng M. Evidence that the regulation of diphtheria toxin production is directed at the level of transcription. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):511–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.511-516.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr, de Borms S. T. Synthesis of diphtheria tox-gene products in Escherichia coli extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):11–15. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. R., Skiver J., McBride G. Isolation and partial characterization of a corynebacteriophage beta, tox operator constitutive-like mutant lysogen of Corynebacterium diphtheriae. J Virol. 1976 Apr;18(1):235–244. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.1.235-244.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. D., Mekalanos J. J. Molecular cloning of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin genes in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2976–2980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar I. K., Nagesha C. N., Bhat J. V. Effect of metal ions on the production of vascular permeability factor by 569B strain of Vibrio cholerae. Indian J Med Res. 1979 Jan;69:18–25. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sagar I. K., Nagesha C. N., Bhat J. V. The role of trace elements and phosphates in the synthesis of vascular-permeability factor by Vibrio cholerae. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Aug;14(3):243–250. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-3-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer E. K., Noble J. A. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin. Nucleotide sequence of the A subunit gene. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5716–5721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporecke I., Castro D., Mekalanos J. J. Genetic mapping of Vibrio cholerae enterotoxin structural genes. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jan;157(1):253–261. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.1.253-261.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida T., Gill D. M., Pappenheimer A. M., Jr Mutation in the structural gene for diphtheria toxin carried by temperate phage . Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 1;233(35):8–11. doi: 10.1038/newbio233008a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward W. E., Gilman R. H., Hornick R. B., Libonati J. P., Cash R. A. Efficacy of a live oral cholera vaccine in human volunteers. Dev Biol Stand. 1976;33:108–112. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]