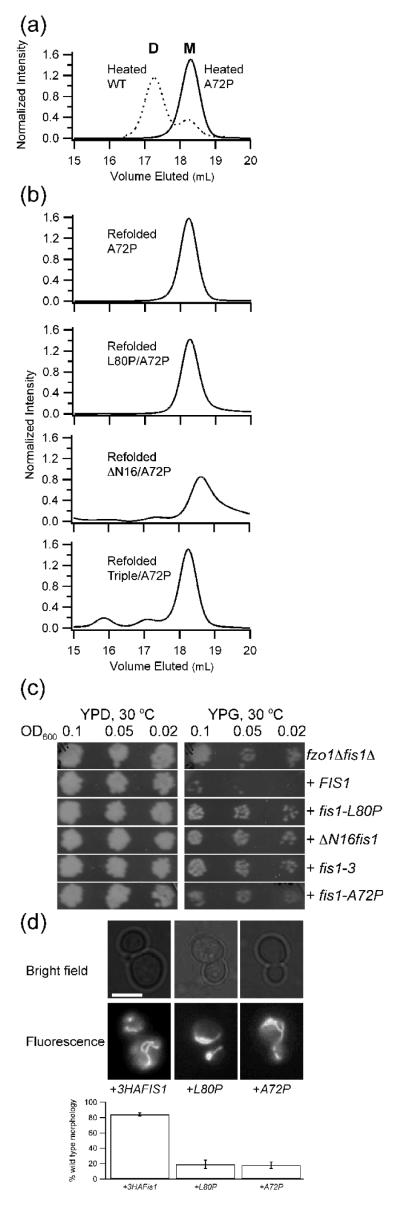
Figure 5. Designed mutant A72P impairs dimerization of Fis1ΔTM and mitochondrial fission.
a) A 2.5 μM sample of Fis1ΔTM-A72P was heated, cooled, and analyzed by size exclusion chromatography as described in Figure 3. For comparison purposes, a similar experiment with wild type Fis1ΔTM is overlaid as a dashed line (from Fig 3a). b) A 2.5 μM sample of Fis1ΔTM-A72P was chemically unfolded in GdHCl, refolded, and analyzed by size exclusion chromatography as described in Figure 3. Introducing A72P into each of the non-functional Fis1ΔTM variants and refolding from chemical denaturant also strongly favored the monomeric state. These variants were well folded (Supplemental Figure 3) indicating a common structural basis for dimerization of each variant. c) Yeast expression of either obligate dimers (ΔN, fis1-3) or obligate monomer (A72P) do not rescue mitochondrial fission. In this standard growth assay, functional fission is signified by no growth on YP+Glycerol (YPG) plates. Note that these are full-length Fis1 constructs that include the C-terminal transmembrane domain. d) Expression of full-length Fis1-A72P in fis1Δ yeast cells impairs mitochondrial morphology to a similar extent as full-length Fis1-L80P expression. Representative epifluorescence microscopy images from fis1Δ yeast cells expressing the indicated plasmids and stained with MitoTracker Red CMXRos. Percentage of cells with wild type morphology is shown based on scoring >100 cells from three independent experiments. Expression of full-length 3xHA-FIS1 rescued 84 ± 2 % of cells compared to 19 ± 5 % for 3xHA-FIS1-L80P and 18 ± 4 % for 3xHA-FIS1-A72P. Scale bar is 5 μm.