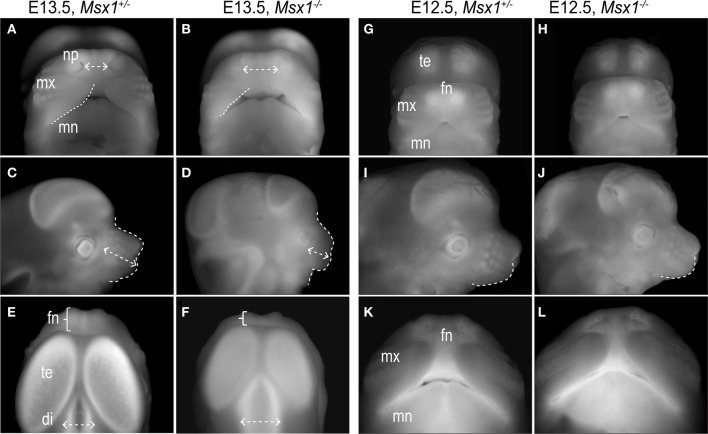
Figure 2.
Facial dysmorphologies in Msx1−/− embryos are detectable at E13.5 but not at E12.5. (A and B) Frontal view of E13.5 Msx1+/− and Msx1−/− embryos. Dashed lines indicate edges of the maxillary prominence and dashed arrows, distance between the nasal pits (internasal pit distance in Table 1). (C and D) Lateral view of Msx1+/− and Msx1−/− embryos. Dashed lines demarcate outline of the maxillary prominence; dashed arrow indicate length of the rostrum (maxillary length in Table 1). (E and F) Dorsal view of Msx1+/− and Msx1−/− embryos; bracket indicates size of the frontonasal prominence. Dashed arrows indicates width of the diencephalon. (G and H) Frontal view of E12.5 Msx1+/− and Msx1−/− embryos. (I and J) Lateral view, where dashed lines demarcates outline of the maxillary prominence. (K and L) Ventral view. di, diencephalon; fn, frontonasal prominence; mn, mandibular prominence; mx, maxillary prominence; np, nasal pit; te, telencephalon.