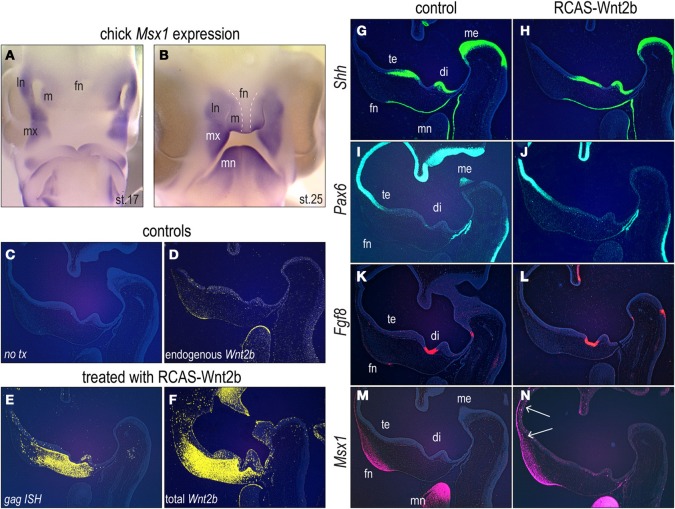
Figure 5.
Wnt2b over-expression leads to ectopic Msx1 in the facial prominences. (A) In situ hybridization for Msx1 in the avian facial prominences at stage 17 HH. (B) In situ hybridization for Msx1 in the avian facial prominences at stage 25 HH. Dashed lines delimit the lack of Msx1 expression in the midline of frontonasal prominence. (C,D) Mid-sagittal section through the head of an uninjected embryo. (D) Endogenous Wnt2b expression in the same embryo. (E) Mid-sagittal section through the head of an embryo, analysed 24 h after RCAS:Wnt2b infection, showing viral delivery to the face. (F) RCAS:Wnt2b infection drives ectopic Wnt2b expression. Forty-eight hours after RCAS:Wnt2b treatment, chicken embryos were assessed for alterations in (G,H), Shh, (I,J) Pax6, (K,L) Fgf8 and (M,N) Msx1 expression. White arrows indicate expanded Msx1 expression domain. Di, diencephalon; fn, frontonasal prominence; ln, lateral nasal prominence; m, medial nasal prominence; mb, midbrain; me, metencephalon; mn, mandibular prominence; mx, maxillary prominence; np, nasal pit; te, telencephalon.