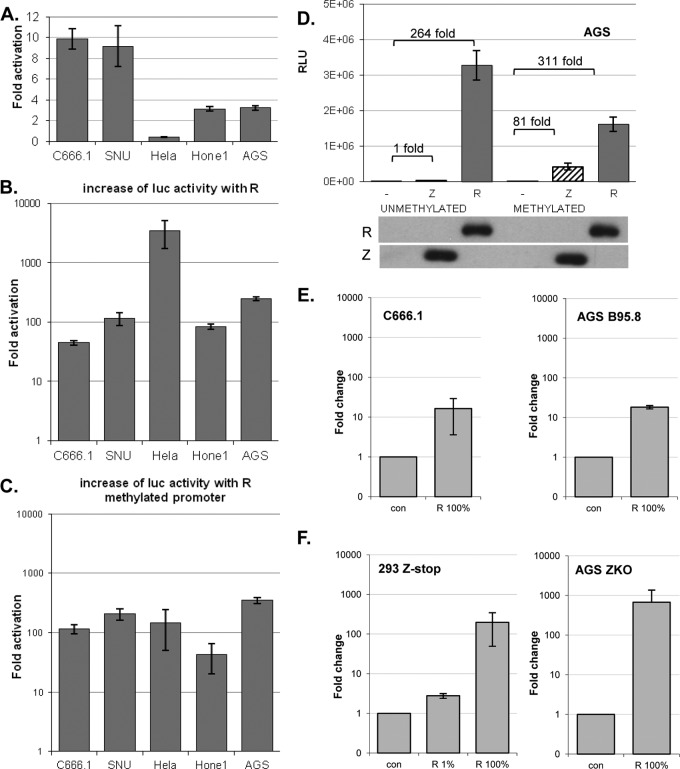
Fig 2.
R, but not Z, activates the BARF1 promoter, independent of methylation status and in the context of the viral genome. A BARF1 promoter reporter construct was created by inserting the promoter sequence up to −679 nucleotides from the ATG start site upstream of the luciferase gene in a CpG-free reporter construct. (A) Luciferase assays showed that the constitutive activity of the BARF1 promoter in pCpG.LUC versus pCpG.LUC empty was highest in EBV-positive C666.1 and SNU-719 cells. (B) Cotransfection of the reporter construct with an R expression vector induced a 50- to 250-fold upregulation of luciferase activity in most cell lines and up to 3,000-fold upregulation in HeLa cells. For HeLa, AGS, and SNU-719 cells, n = 2; for C666.1 and Hone1 cells, n = 3. Standard errors of the means (SEM) are shown. (C) An ex vitro-methylated reporter construct maintained its activation when cotransfected with an R expression vector. (D) Representative example of unmethylated or methylated promoter construct cotransfected either with an R or Z expression vector in AGS cells. Both empty vector (−) and R vector relative light unit (RLU) values were lower when the promoter luciferase construct was methylated, leaving the fold activation mostly unaffected. SDS-PAGE Western blot analysis confirmed equal expression levels of Z and R protein. (E) EBV-positive C666.1 and AGS B95-8 cells expressed more BARF1 mRNA 48 h after transfection with R, indicating that R upregulates BARF1 in the context of EBV infection. con, control. (F) Parallel experiments using Z-defective HEK293 cells (Z-stop) and Z knockout (ZKO) AGS cells demonstrated autonomous R-transactivating activity of BARF1 that was independent of the lytic cycle. When only 1% of the transfected DNA consisted of R expression vector, induction of BARF1 was reduced, indicating that BARF1 induction was R dosage dependent.