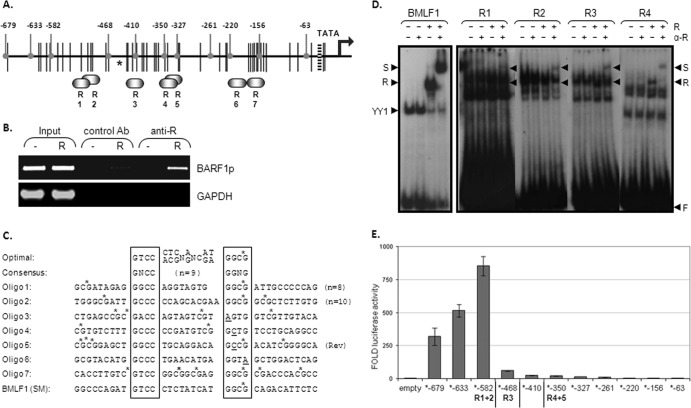
Fig 3.
R binds to RREs on the BARF1 promoter. (A) Potential R-responsive elements (R1 to R7) are depicted on the BARF1 promoter region. Black vertical lines represent methylation sites. Rounded gray indicators point to the deletion mutants made from the BARF1 reporter construct, shortening the BARF1 promoter sequence from the original −679 to −63 relative to the ATG start site. The asterisk indicates the R ChIP sequence peak as determined by Heilman et al. (25). (B) ChIP assays were performed using extracts from HEK293 BRLF1-stop cells transfected with an R expression vector (R) or a control vector (−). R was immunoprecipitated by a control antibody (Ab) or anti-R antibody, and coimmunoprecipitated DNA was PCR amplified. The band in the last lane indicates that the BARF1 promoter region DNA specifically precipitated with R. (C) The RRE optimal sequence and the consensus sequence according to Chen et al. (11) are shown. Oligonucleotides of the potential RREs in the BARF1 promoter with surrounding nucleotides were used in EMSA. To create double-stranded probes, oligonucleotides were hybridized with their respective opposite strands. The oligonucleotide of the BMLF1 promoter RRE served as a positive control. CpG sites are indicated by stars. (D) The ability of in vitro-translated C-terminal-truncated R (R550) to bind to 23P-end-labeled probes of the potential RREs in the BARF1 promoter was examined by EMSA. Extracts were made of HeLa cells transfected with a control (−) or with R550 (+). A probe containing the BMLF1 promoter RRE served as a positive control. Four of the seven RREs (RRE 1 to 4) on the BARF1 promoter showed binding (R). S, supershift; F, unbound oligonucleotide. (E) Deletion mutants of the BARF1 promoter reporter construct were made as indicated in panel B. AGS cells were transfected with the deletion mutant luciferase constructs and with or without R expression vector. The R-induced luciferase activity (fold) was measured 48 h after transfection. Data represent the results of a representative experiment.