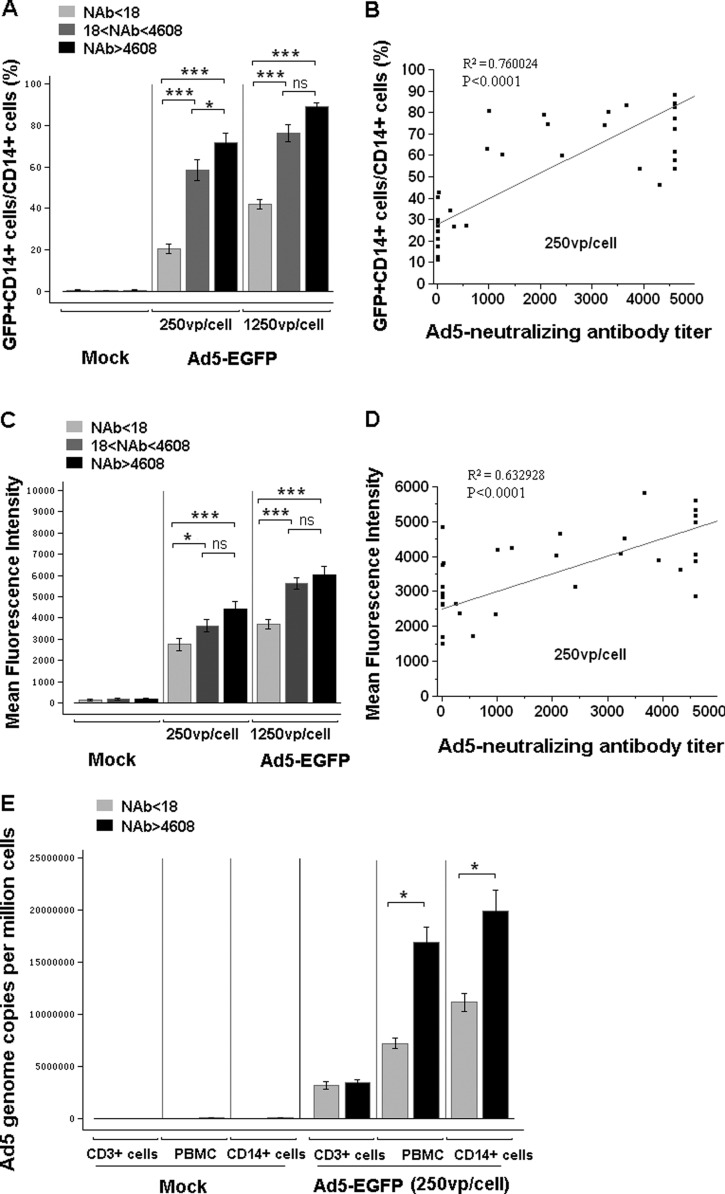
Fig 2.
CD14+ cells in human PBMCs from Ad5-seropositive people were more susceptible to Ad5 infection than those from Ad5-seronegative people. Human PBMCs were infected with Ad5-EGFP at 0 vp/cell, 250 vp/cell, and 1,250 vp/cell. The subjects were divided into three groups based on the level of preexisting NAb: Ad5 NAb naïve (NAb < 18; n = 11), Ad5 NAb median (18 < NAb titer < 4,608; n = 15), and Ad5 NAb high (NAb titer > 4,608; n = 8). Expression of EGFP in CD14+ cells was analyzed by FACS at 24 h postinfection. (A) Percentage of EGFP-positive cells in CD14+ cell population. (C) EGFP expression level of the CD14+ cell population. These data were analyzed statistically by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. Correlations of the percentage (B) or EGFP expression level (D) of CD14+ EGFP-positive cells in PBMCs with adenovirus-neutralizing antibody titer were determined using linear fit analysis. (E) Ad5 genome copy number in PBMCs from Ad5-seronegative (n = 4) or Ad5-seropositive (n = 4) people was determined by quantitative PCR after infection at 250 vp/cell. These data were analyzed statistically by a nonparametric Mann-Whitney U test. The bars represent the standard errors. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, no significance.