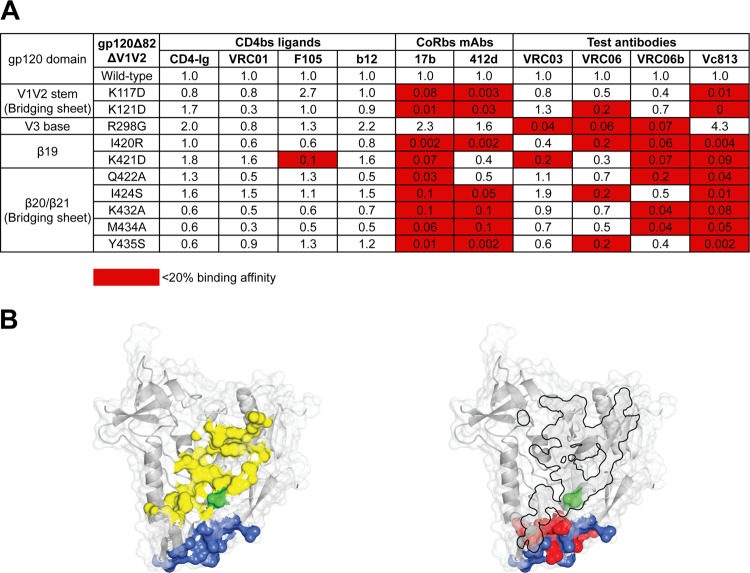
Fig 4.
VRC06 and related MAbs' binding specificity for the CoRbs. (A) Fine mapping of VRC06 and VRC06b binding specificity for point mutations in the CoRbs, including the bridging sheets and V3 base, in the context of the YU2 gp120 Δ82ΔV1V2 glycoprotein by ELISA. The binding affinity of MAbs for the YU2 gp120 Δ82ΔV1V2 mutant proteins compared to that for the wild-type protein was calculated as described in the legend for Fig. 3. Mutations in the CoRbs regions affected VRC06 and VRC06b binding, similar to other CoRbs MAbs, but had no effect on CD4bs ligands, suggesting that the epitopes of VRC06 and VRC06b were functionally or structurally related to the CoRbs of gp120. (B) CD4bs and CoRbs on the gp120 core surface. Left, CD4 footprint (yellow) and CoRbs MAb 17b footprint (blue) on the gp120 core surface (Protein Data Bank [PDB], 2NY3). The prototypic residue in the CD4bs, D368, is in green, and VRC06 and VRC06b are sensitive to mutations at this residue. Right, the VRC03 footprint from the published structure (PDB, 3SE8) shown on the molecular surface of the gp120 core (PDB, 2NY3) as a black-bordered area. The residues identified in panel A affecting VRC06 and VRC06b binding to the YU2 gp120 Δ82ΔV1V2 that are located in the bridging sheet area are shown in red. Note that the VRC03 footprint has some limited overlap with the footprint of 17b (blue), while the Ala scan-inferred footprints of VRC06 and VRC06b in the bridging sheet demonstrate more overlap with the 17b footprint. The Ala scan-inferred footprints of VRC06 and VRC06b contain the prototypic CD4bs residue, D368, as does the footprint of VRC03.