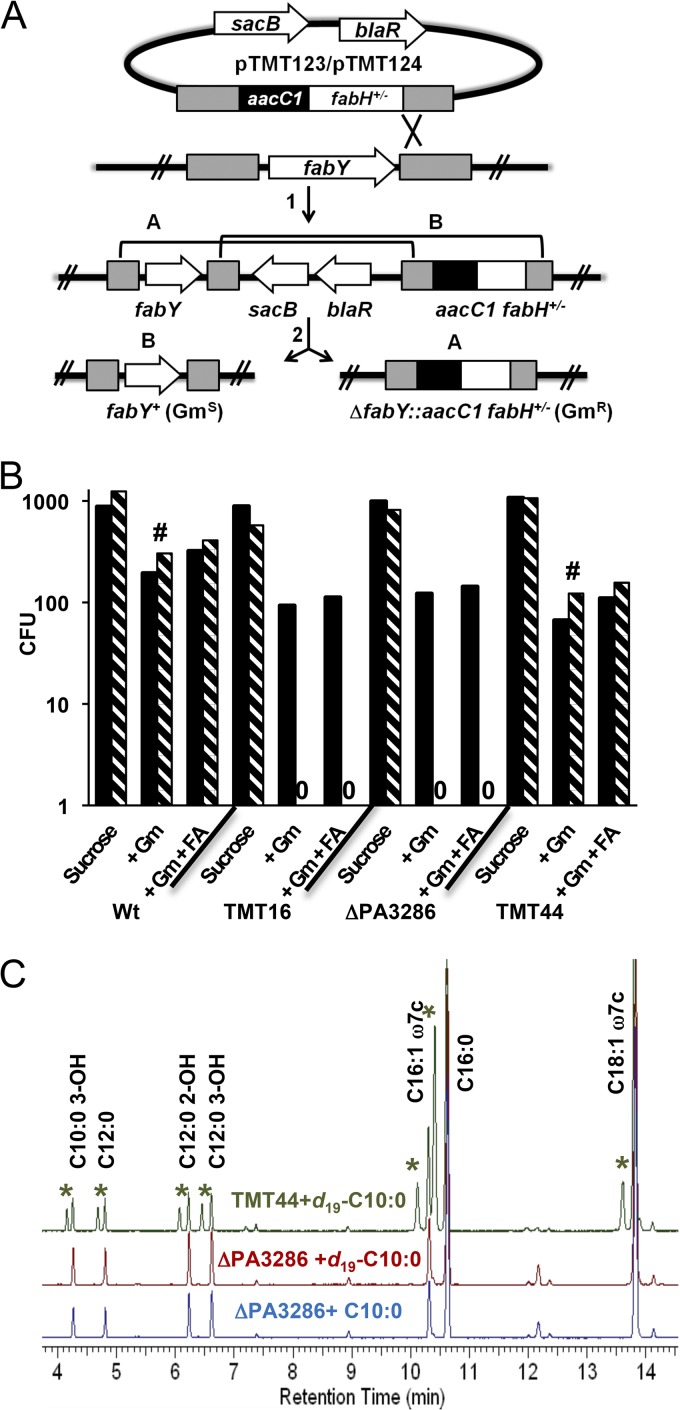
Fig 4.
Synthetic lethal analysis for fabY with KASIII domain fabH orthologs and fatty acid rescue. (A) Vectors conferring aacC1-mediated gentamicin (Gm) resistance that targeted the P. aeruginosa fabY gene were designed to either exchange fabH of E. coli (pTMT123 fabH+) or to delete fabY (pTMT124). Merodiploid intermediates (after step 1) were confirmed by PCR analysis and passively resolved by outgrowth in LB medium (step 2). Aliquots were plated on LB-sucrose agar to counterselect unresolved clones and to enumerate the sum of A- and B-type recombination events. In parallel, aliquots were plated on LB-sucrose agar plus Gm and on LB-sucrose agar plus Gm with 100 μg/ml of the fatty acid supplement decanoate (FA) to select only the recombinants arising through A-type recombination. (B) The pTMT123/124 vectors were individually introduced into the wild-type (Wt) P. aeruginosa, TMT16 (ΔPA0998 ΔPA0999 ΔPA3333 ΔPA3286), ΔPA3286, and TMT44 (ΔPA3286 attB::PA3286+). CFU resulting from resolving either pTMT123 (black bars) or pTMT124 (hatched bars) were determined by counting colonies that appeared after 24 h or 48 h (#) of incubation at 37°C. The selection media and strain background are indicated below the x axis. Data are representative of 3 separate experiments. The results for the ΔPA0998, ΔPA0999, and ΔPA3333 mutant strains are shown in Fig. S2 in the supplemental material. (C) Gas chromatograms with FID detection of FAME extracts obtained from P. aeruginosa strains grown on LB agar with either 100 μg/ml of decanoate (C10:0) or perdeuterated decanoate (d19-C10:0). Asterisks indicate FAME peaks unique to d19-C10:0-fed samples with structures assigned as in Fig. 3.