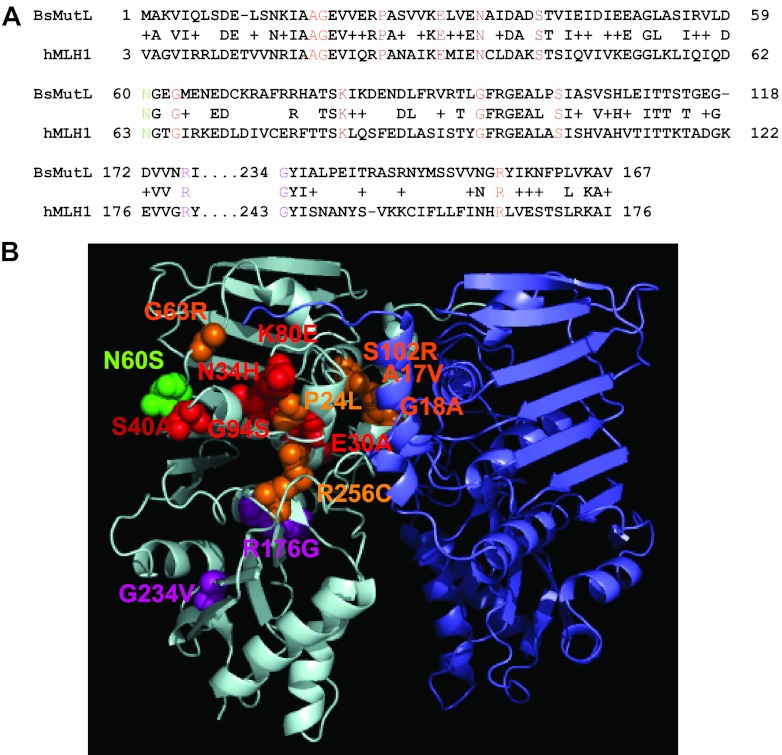
Fig 1.
Homology model of B. subtilis MutL N-terminal domain with the locations of amino acid substitutions indicated. (A) A sequence alignment of the N-terminal domains of B. subtilis MutL (BsMutL) and human MLH1 (hMLH1) is shown. We show the primary structure alignment relevant to the location of the missense mutations that were tested in this study. Colored residues correspond to the colors used in panel B. (B) A model of the MutL N-terminal domain dimer is shown. The amino acid residue changes are modeled on the left monomer. Residues predicted to be important for ATP binding, ATP hydrolysis, and DNA binding are colored in orange, red, and purple, respectively. Mutants with functions that are unclear based on homology are colored in green.