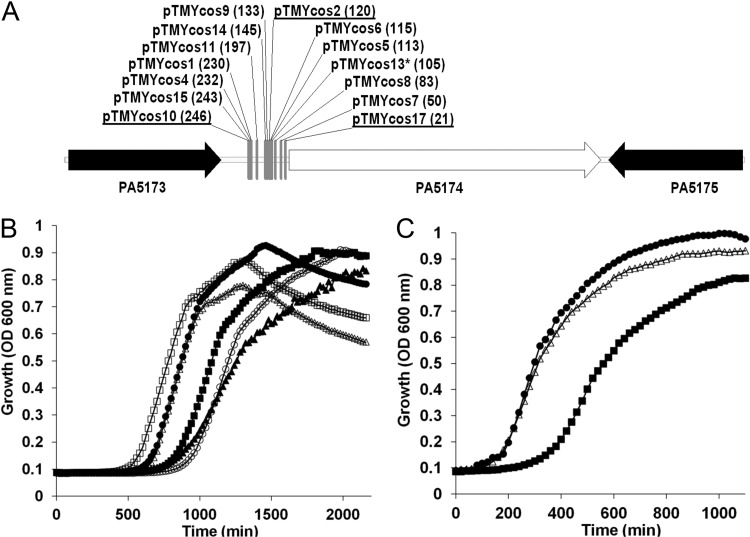
Fig 3.
Complementation of FabH depletion in E. coli K-12 by a P. aeruginosa cosmid library. (A) The plasmid-genomic DNA insert junction sites of cosmids that rescued growth of the FabH-depleted E. coli strain TMY19. All 14 sites were located in the immediate 5′ intergenic region of the unknown open reading frame PA5174 and contained 24 to 42 kb of downstream DNA. All inserts except for pTMYcos13 (asterisk) placed PA5174 proximal to the T7 promoter on the pWEB vector backbone. The number of base pairs intervening between the respective cosmid-junction site and the start codon of PA5174 is indicated in parentheses. Cosmids selected for further growth analysis are underlined. (B) Growth curves of E. coli strain TMY19 grown in various conditions at 37°C. E. coli TMY19 was grown in LB only (▲) or in LB plus 0.2% l-arabinose inducer (△). E. coli TMY19 was grown in LB plus 0.2% l-arabinose inducer with cosmid pTMY2 (●), cosmid pTMY10 (■), cosmid pTMY17 (○) or plasmid pWEB-PA5174 (□). (C) Growth curves of the IPTG-inducible PA5174 E. coli strain TMY32 with fabH deleted in LB (in the absence of IPTG [■] or in the presence of 1 mM IPTG [△]) were measured at 37°C in LB and compared to that of the parent wild-type strain BW25113 (●).