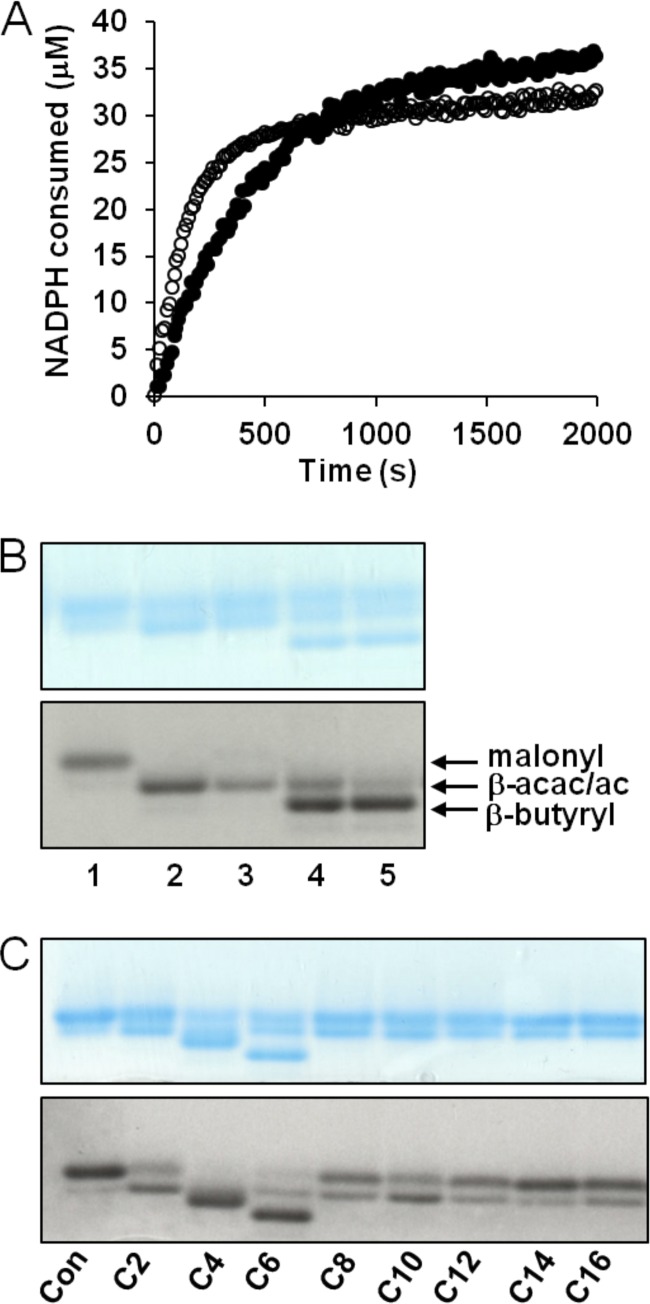
Fig 8.
Enzymatic activity and acyl-CoA acceptor substrate specificity of recombinant PA5174. (A) The continuous FabG coupled assay was initiated with 15 nM FabH (●) or PA5174 (○), and the reaction mixture was incubated at 30°C. Reaction progress was monitored by UV absorbance at 340 nm to assay NADPH consumption. Background absorbance (no enzyme addition) was subtracted from each curve before plotting. (B) Discontinuous conformation-sensitive urea-PAGE was employed to separate acyl-ACP products with incorporated [2-3H]malonyl-ACP substrate. Gels were sequentially imaged using Coomassie blue staining and autoradiography. All lanes contained [2-3H]malonyl-ACP and acetyl-CoA substrates. Lanes: 1, substrates only; 2, E. coli FabH; 3, PA5174; 4, E. coli FabH plus FabG/FabA/FabI; 5, PA5174 plus FabG/FabA/FabI. The positions of malonyl-ACP (malonyl), β-acetoacetyl-ACP or acetyl-ACP (β-acac/ac), and β-butyryl-ACP (β-butyryl) are labeled. (C) The acyl-CoA substrate specificity of PA5174 was assayed using [2-3H]malonyl-ACP substrate alone (control [Con]) or with various acyl-CoA acceptors (C2 to C16). Reaction products were separated by urea-PAGE, stained, and sequentially imaged. Under these assay conditions, the [2-3H]β-acetoacetyl-ACP reaction product using C2-CoA as the acceptor is not adequately separated from the [2-3H]acetyl-ACP side product produced by decarboxylation of [2-3H]malonyl-ACP unless further reduced by FabG/FabA/FabI as in lanes 4 and 5 of panel B.