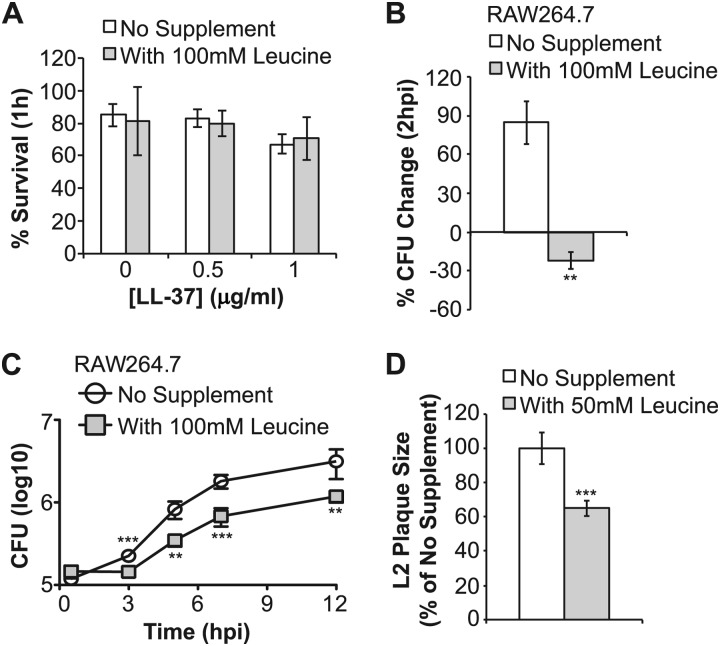
Fig 6.
Leucine supplementation in WT L. monocytogenes compromises virulence but not CAMP resistance. To further investigate whether specific BCFA composition is necessary to confer resistance, WT bacteria were cultured in the presence of leucine to decrease the ratio between anteiso- and iso-BCFA. (A) Resistance to LL-37 was determined by calculating survival of WT bacteria grown in BHI or in BHI + 100 mM leucine by comparing CFU before and after 1 h of exposure. (B) Resistance to macrophage killing was determined by calculating the percent CFU change between 0.5 and 2 hpi in RAW 264.7 cells. The data plotted represent averages of three independent experiments, with error bars denoting the standard deviation. Each independent experiment was performed with triplicates. (C) The effect of leucine supplementation on intracellular growth was determined by infecting RAW 264.7 macrophages and enumerating intracellular CFU during a time course of 12 hpi. Averages of triplicates were plotted, with error bars denoting standard deviation. The data shown represent at least two independent experiments. (D) We infected a monolayer of L2 fibroblasts with WT L. monocytogenes in the presence or absence of 100 mM leucine and compared the size of areas of clearance (plaques) caused by lysed cells. The data shown represent at least two independent experiments. Significant differences are indicated by asterisks (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.005).