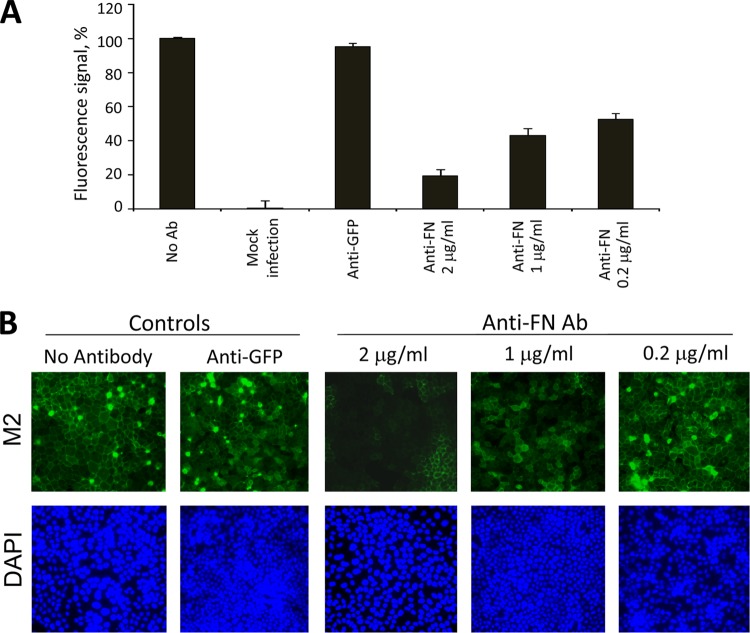
Fig 6.
Anti-FN antibody inhibits postattachment events of H1N1. (A) Anti-FN antibodies inhibit membrane fusion. WSN-infected cells were incubated with various concentrations of anti-FN antibodies. Membrane fusion was induced by a brief acid wash. The amount of fused RBCs was measured, as described in Materials and Methods. Mock-infected cells (Mock), infected cells treated with 2 μg of anti-GFP/ml (anti-GFP) and infected cells with no antibody (No Ab) were used as controls in the experiment. The signal from infected cells, but without antibody treatment, was set as 100%. (B) Anti-FN can inhibit the viral entry of WSN. A viral postattachment assay was performed as described in Materials and Methods. The cells were incubated at 37°C for 8 h after antibody treatment. Fixed cells were strained for M2 (green) and DAPI (blue).