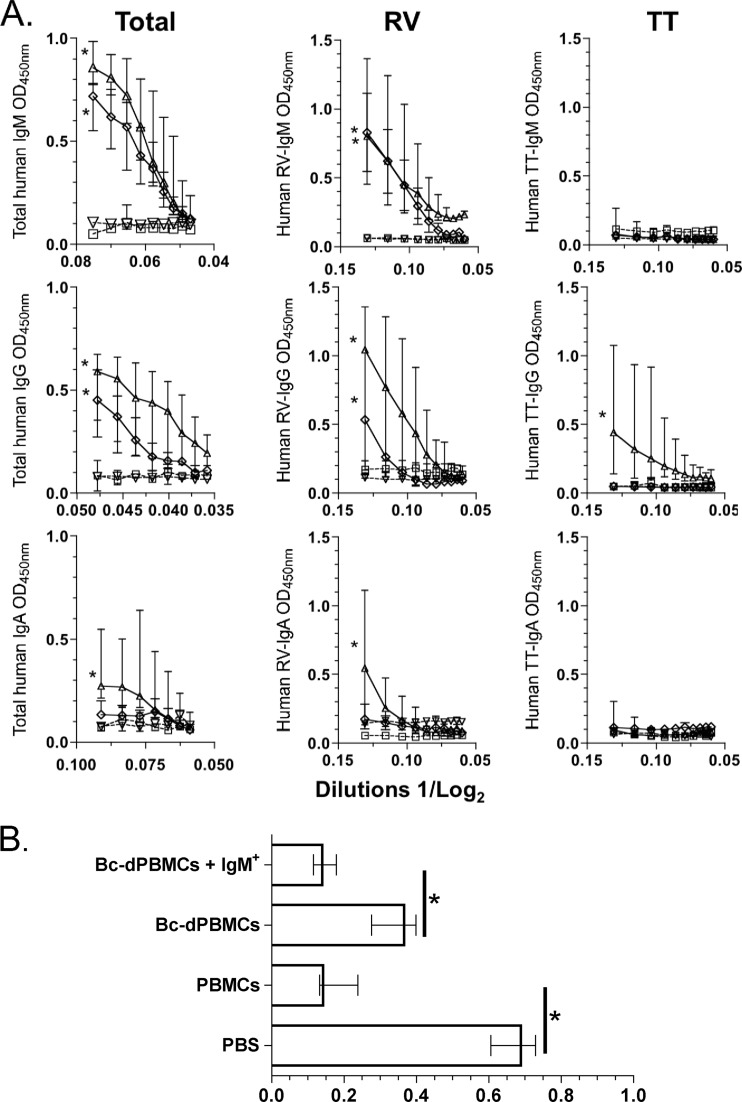
Fig 3.
Total and RV IgM+ mBc switch to IgG isotype frequencies in vivo. (A) Immunodeficient NOD/Shi-scid IL-2Rγnull adult mice were i.p. inoculated with PBS (□, dashed line), PBMCs (△, continuous line), Bc-dPBMCs (▽, dashed line), or Bc-dPBMCs plus highly purified IgM+ mBc (♢, continuous line) and immediately infected orally with the murine ECWT strain RV. Fifteen days after infection, relative quantities of human total, RV-specific, and tetanus toxoid (TT)-specific (as a control Ag) IgM, IgG, and IgA were determined in the serum by ELISA. Optical densities (at 450 nm) of serial dilutions of serum are presented on a log2 scale. Each point represents the median (n = 4), and the lines represent the range for each dilution. An asterisk represents a statistically significant difference (P < 0.05, Mann-Whitney test). (B) Human IgM+ mBc are involved in clearing RV antigenemia. Relative quantities are shown for RV VP6 detected by ELISA (optical density at 450 nm [OD450]) in the serum of mice that were transferred human cells (or PBS as a control). The bars represent the medians, and lines represent the ranges (n = 4). An asterisk indicates a significant difference (P = 0.02, Mann-Whitney test).