Abstract
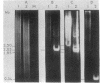
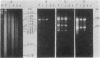
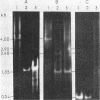
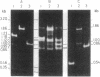
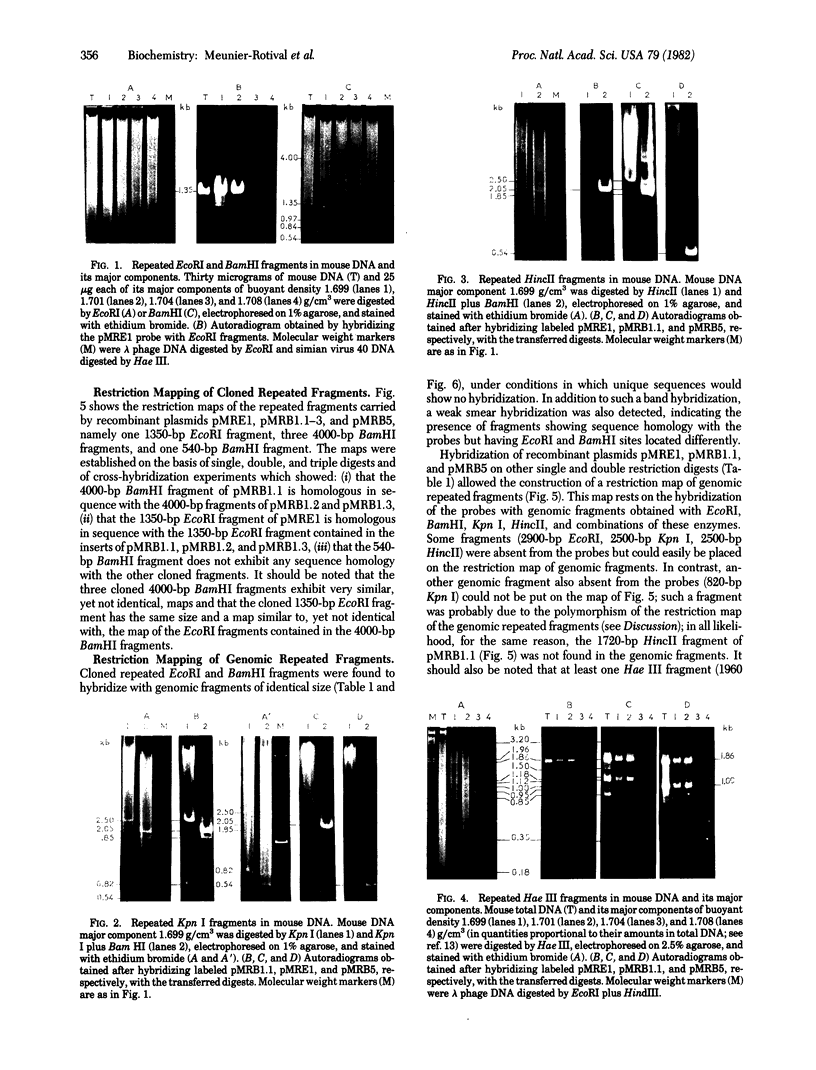
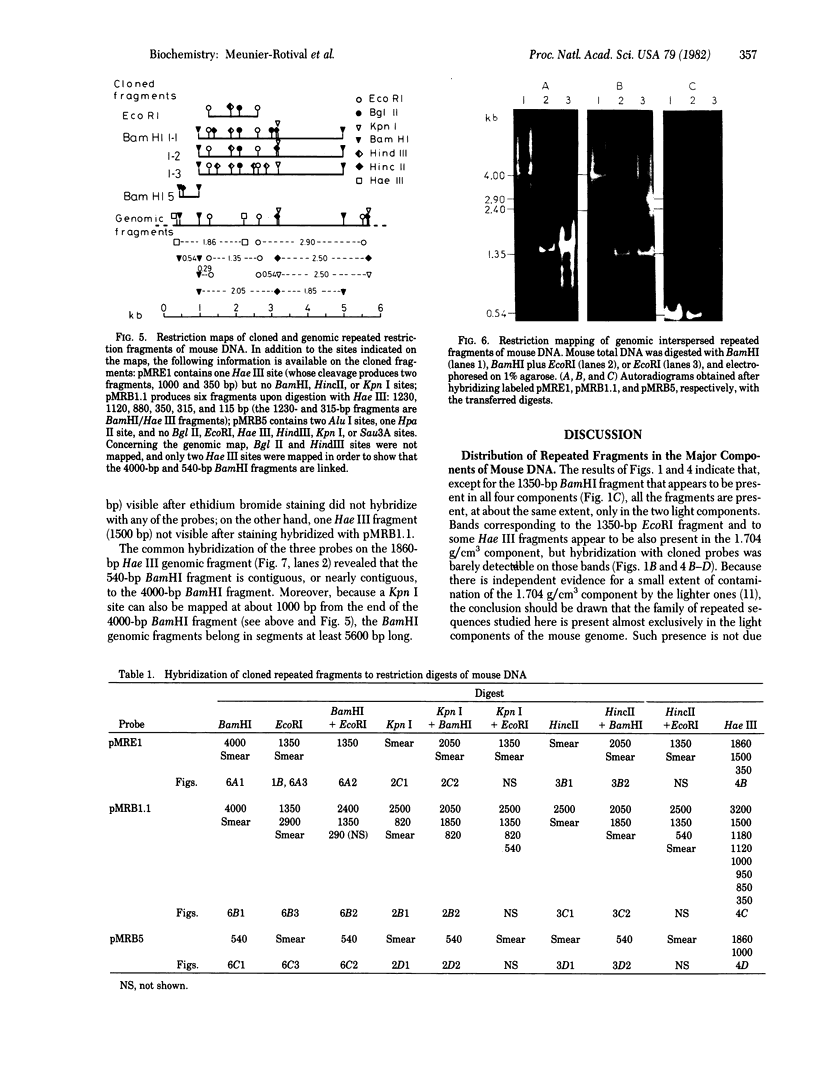
We have investigated that organization and the distribution of a family of interspersed DNA repeats in the mouse genome. The repeats are at least 5600 base pairs (bp) in size and contain two contiguous BamHI endonuclease fragments, 4000 and 540 bp in size, the larger of which includes a 1350-bp EcoRI fragment studied by previous authors. The repeats are polymorphic in their restriction maps, and represent the major family of interspersed repeats in the mouse genome. The repeats are present almost exclusively in the two light major components of mouse DNA, and the base composition of their large BamHI fragments matches that of those components. The genomic distribution of the repeats is different from that of structural genes, which are present not only in the two light components but also in the two heavy components of mouse DNA. This distribution indicates that the repeats are not involved, at least in any simple way, in the regulation of gene expression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blin N., Stafford D. W. A general method for isolation of high molecular weight DNA from eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2303–2308. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. D., Dover G. Organization and evolutionary progress of a dispersed repetitive family of sequences in widely separated rodent genomes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 25;150(4):441–466. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90374-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. M., Schildkraut C. L. A family of moderately repetitive sequences in mouse DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4075–4090. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortadas J., Olofsson B., Meunier-Rotival M., Macaya G., Bernardi G. THE DNA components of the chicken genome. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 15;99(1):179–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13244.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuny G., Soriano P., Macaya G., Bernardi G. The major components of the mouse and human genomes. 1. Preparation, basic properties and compositional heterogeneity. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):227–233. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05227.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipski J., Thiery J. P., Bernardi G. An analysis of the bovine genome by Cs2SO4-Ag density gradient centrifugation. J Mol Biol. 1973 Oct 15;80(1):177–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90240-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haigwood N. L., Jahn C. L., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Edgell M. H. Locations of three repetitive sequence families found in BALB/c adult beta-globin clones. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1133–1150. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heller R., Arnheim N. Structure and organization of the highly repeated and interspersed 1.3 kb EcoRI-Bg1II sequence family in mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):5031–5042. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.5031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson A. P., Cuny G., Cortadas J., Haschemeyer A. E., Bernardi G. An analysis of fish genomes by density gradient centrifugation. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Nov;112(2):203–210. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb07195.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörz W., Hess I., Zachau H. G. Highly regular arrangement of a restriction-nuclease-sensitive site in rodent satellite DNAs. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):501–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macaya G., Thiery J. P., Bernardi G. An approach to the organization of eukaryotic genomes at a macromolecular level. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov;108(1):237–254. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80105-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Novel classes of mouse repeated DNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Aug 11;8(15):3247–3258. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.15.3247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meunier-Rotival M., Cortadas J., Macaya G., Bernardi G. Isolation and organization of calf ribosomal DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979;6(6):2109–2123. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.6.2109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soriano P., Macaya G., Bernardi G. The major components of the mouse and human genomes. 2. Reassociation kinetics. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Apr;115(2):235–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Long range periodicities in mouse satellite DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 5;94(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90404-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Macaya G., Bernardi G. An analysis of eukaryotic genomes by density gradient centrifugation. J Mol Biol. 1976 Nov;108(1):219–235. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80104-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]