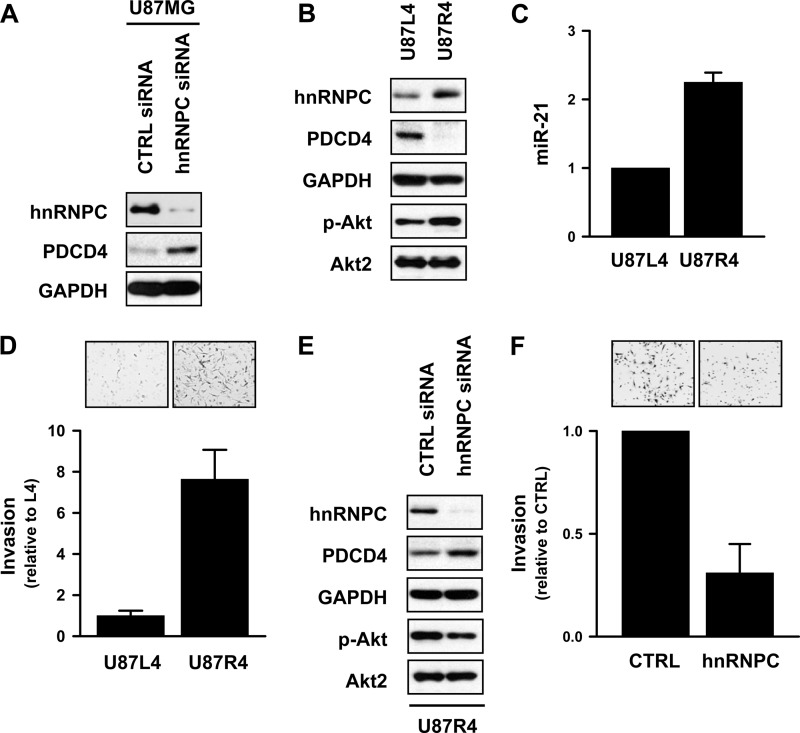
Fig 6.
hnRNPC is overexpressed in highly invasive U87MG (U87R4) cells. (A) PTEN-deficient glioma cell line U87MG was transfected with control (CTRL) or hnRNPC siRNAs, and 48 h later, the levels of hnRNPC and PDCD4 were determined by Western blot analysis. (B) To compare the expression of hnRNPC and PDCD4 in U87L4 cells relative to their levels in U87R4 cells, whole-cell lysates were prepared and the levels of hnRNPC, PDCD4, p-Akt, Akt2, and GAPDH expression were determined by Western blot analysis. (C) The levels of miR-21 in U87L4 and U87R4 cells were determined by RT-qPCR using the TaqMan microRNA assay kit. (D) To isolate highly invasive U87R4 cells, U87MG cells were subjected to serial intracranial injection. After 4 cycles of selection, U87L4 (nonmigrating) and U87R4 (migrating) cells were isolated. Equal cell numbers of each cell population were added into a Biocoat Matrigel invasion chamber; 24 h later, invaded cells were stained and photographed under a microscope. The inhibitory activity of hnRNPC was determined by counting the average number of invaded cells from 9 different fields. Data are means and standard deviations from three different experiments. (E) U87R4 (migrating) cells were transfected with control (CTRL) or hnRNPC siRNAs, and 48 h later, the levels of hnRNPC, PDCD4, p-Akt, Akt2, and GAPDH expression were determined by Western blot analysis. (F) U87R4 cells were transfected as described above, and invasive activity was determined by counting numbers of invaded cells from 9 different fields.