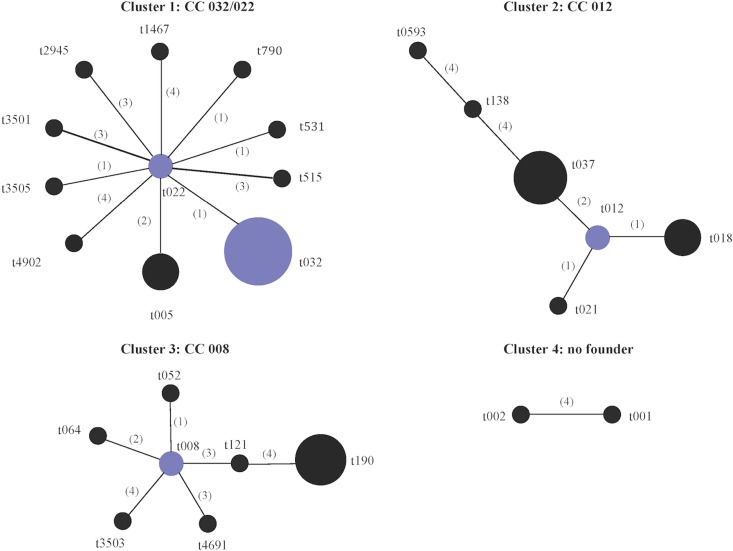
Fig 1.
Based Upon Repeat Pattern (BURP) analysis of the spa types identified among 175 MRSA isolates representative of the different antibiogram-resistogram, sequence type, and SCCmec type combinations recovered from patients in Irish hospitals between 1971 and 2004. Twenty-six of the 35 spa types were grouped into four cluster groups using the BURP algorithm. spa types were clustered together if they contained five or more spa repeats and if they had a cost value of ≤4, where cost accounts for the number of steps of evolution between spa types. A low cost value indicates close evolutionary relatedness between two spa types. The following six spa types were defined as singletons by BURP (t045, t160, t902, t3504, t3506, and t4253), as they could not be clustered with any other spa type, i.e., cost value of ≥5. The spa types t727, t1802, and t2196 were excluded, as they consisted of four repeat units only. Cost values are shown in parentheses. Group founders and cofounders (spa types with the second-highest group founder score) are shown in blue and are determined based on the spa type that shares the highest sequence identity with the greatest number of spa types within that cluster as determined by the cost values. No founder was assigned to cluster 4.