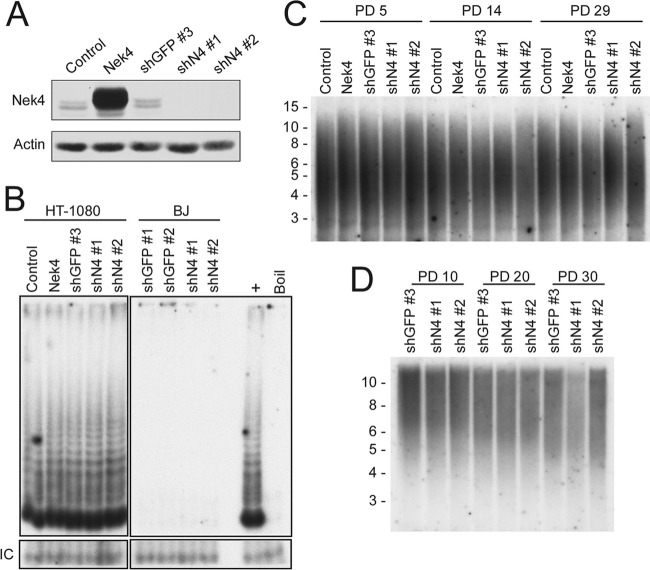
Fig 3.
Effects of NEK4 suppression on telomerase and the telomere. (A) Nek4 overexpression and suppression in HT-1080 cells. HT-1080 cells were infected with either a control vector, a Nek4 overexpression construct, a control shRNA (shGFP no. 3), or each of two NEK4-specific shRNAs (shN4 no. 1 and shN4 no. 2), as indicated. Nek4 levels were measured by immunoblotting. β-Actin is shown as a loading control. (B) Telomerase activity in the presence of Nek4 overexpression or suppression. The telomere repeat amplification protocol was utilized to measure telomerase activity from 2 μg of lysates from HT-1080 cells, shown in panel A, or BJ cells, as indicated. An internal control (IC) for PCR inhibition is shown (bottom), as is a negative control for heat-inactivated lysate (Boil). (C) Telomere length Southern blot of HT-1080 cells. HT-1080 cells, shown in panel A, were cultured for 5, 14, or 29 PD postselection. DNAs collected from these cultures were subjected to TRF Southern blotting, and the intensity of hybridization is shown. Size markers in kb are shown on the left. (D) Telomere length Southern blot of BJ cells. BJ cells expressing control or NEK4-specific shRNAs were cultured for 10, 20, or 30 PD postselection, and the DNA collected was subjected to TRF Southern blotting as in panel C.