Figure 3. Reactivity- and enantioselectivity- dependence on the presence and the acidity of a N-H bond in the nucleophile.
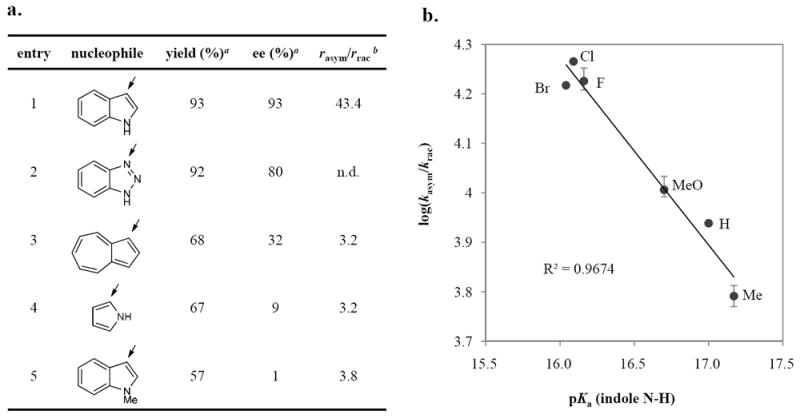
a. Structure-reactivity and -enantioselectivity relationship of p-nucleophiles. a Yields and enantiomeric excesses were obtained under reaction conditions described in eq. 2. b The initial reaction rates with 4-NBSA alone (rrac) and with 4-NBSA/3e (rasym) were determined directly by in situ IR spectroscopy. The (rasym/rrac) value was not determined for benzotriazole (entry 2) because the kinetic analysis was complicated by the poor solubility of the nucleophile in the reaction medium. b. Correlation between the degree of rate acceleration by 3e over the background racemic reaction (kasym/krac) and the acidity of the N-H motif of 5-substituted indole derivatives (pKa). The rate data were obtained by in situ IR and 1H NMR spectroscopy (see Supplementary Information, Section 14 for detailed experimental procedure and data analysis). Error bars reflect the range of experimental data from 2-3 individual measurements, and the line represents the least-squares fit.
