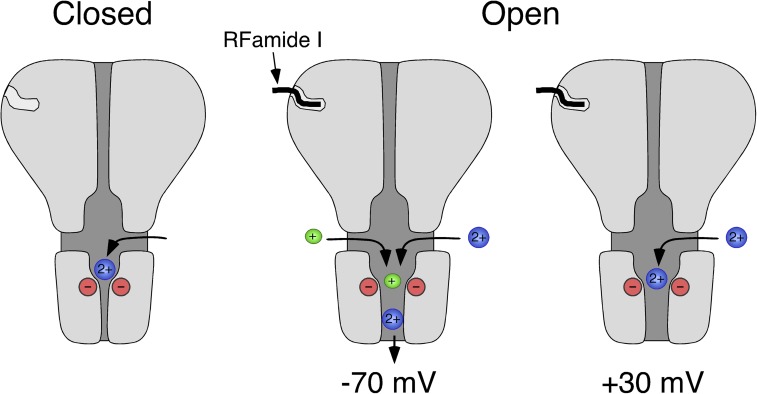
Figure 8.
Scheme illustrating Ca2+ permeation through HyNaC. In the closed conformation (left), Ca2+ can probably access the extracellular vestibule through three lateral fenestrations (Jasti et al., 2007; Li et al., 2011) and bind to the conserved aspartates at the outer mouth of the ion pore. After binding of the ligand, HyNaC opens and, at negative membrane potentials, Ca2+ permeates the channel (−70 mV, middle), liberating the ion pore. At depolarized potentials (+30 mV, right), however, Ca2+ remains bound to the ring of negative charges and blocks the open pore. Based on the crystal structure of chicken ASIC1 (Jasti et al., 2007).