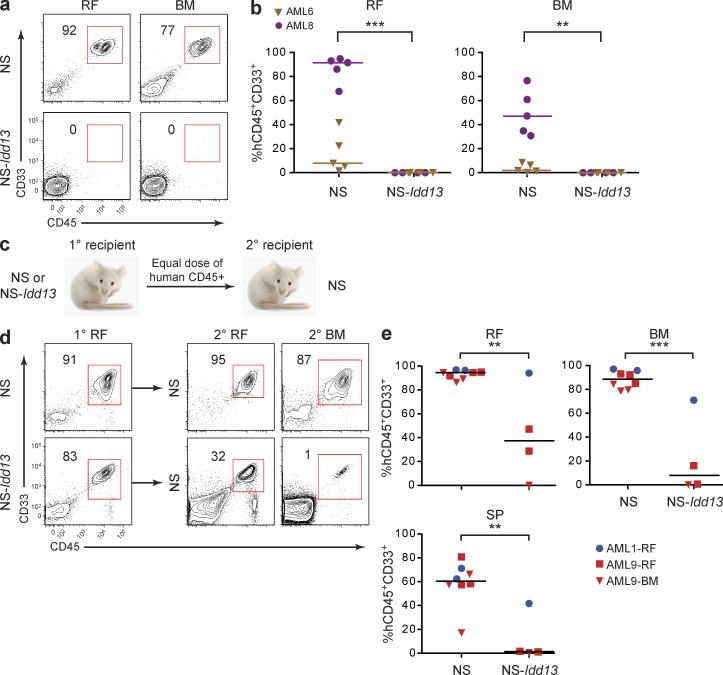
Figure 3.
LSC engraftment and serial transplantation ability depend on NOD-derived SIRPα. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of live cells in the right femur (RF) and noninjected BM of NS and NS-Idd13 mice 8 wk after transplantation of CD34+CD38− cells from sample AML8 into the RF. (b) Summary of human leukemic engraftment in the RF and noninjected BM 8 wk after transplantation of AML cells from two patient samples (AML6 and AML8) into the RF of NS (n = 10) and NS-Idd13 (n = 8) mice. (c) Protocol for serial transplantation of human AML cells harvested from primary NS and NS-Idd13 mice into secondary NS mice. Equal numbers of human CD45+ cells harvested from the injected RF or noninjected BM of primary engrafted NS or NS-Idd13 were injected into the RF of secondary NS mice. (d) Flow cytometric analysis of live cells harvested from the injected RF of primary NS and NS-Idd13 mice and the injected RF and noninjected BM of secondary NS recipient mice. Representative plots are from sample AML9-RF. (e) Summary of human leukemic engraftment in the injected RF, noninjected BM, and SP of secondary NS mice 10 wk after transplantation of AML cells from two patient samples harvested from primary NS (n = 8) and NS-Idd13 (n = 4) mice. (a and d) The percentage of human CD45+CD33+ cells in the live cell gate is indicated. (b and e) Each symbol represents one mouse. Bars indicate median values. **, P < 0.01; and ***, P < 0.001 (Wald test).