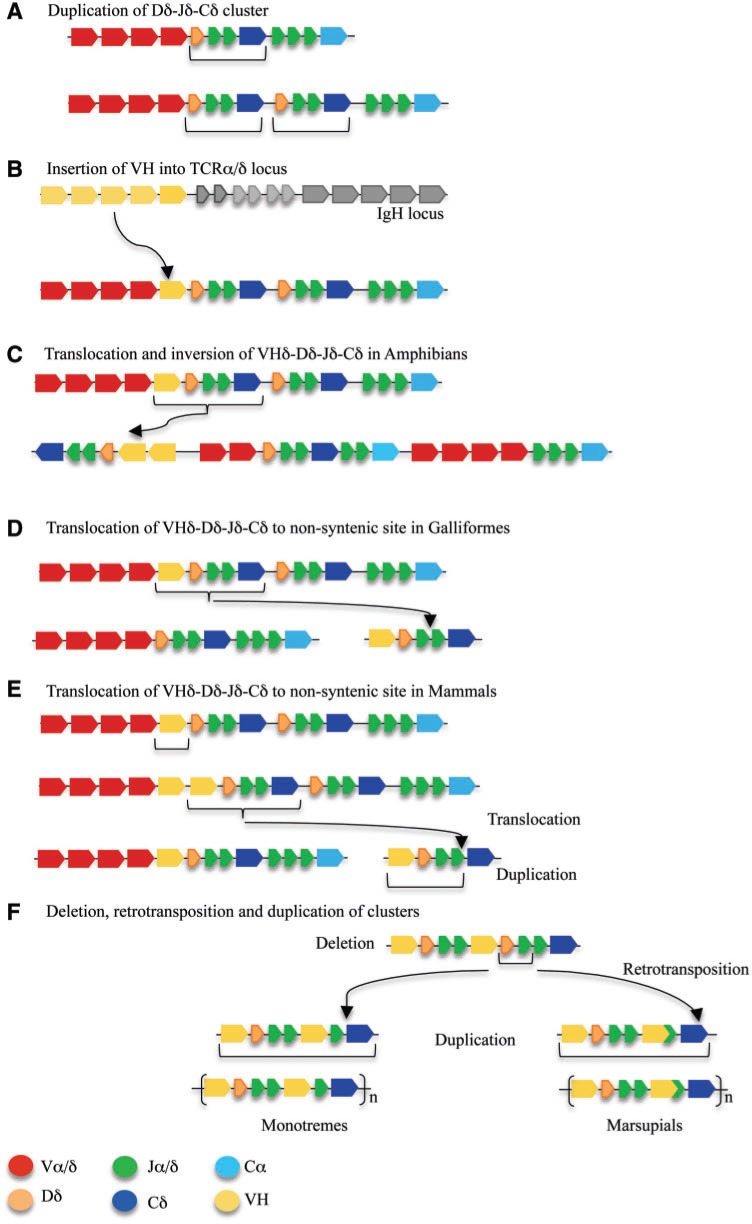
Fig. 5.
A model of the stages of evolution of the TCRα/δ loci in tetrapods and the origins of TCRµ in mammals. A color key of the gene segments is presented at the bottom. (A) Depiction of the Dδ-Jδ-Cδ duplication in an ancestral TCRα/δ locus that provides a second Cδ gene found in frogs and zebra finch. (B) Depiction of the insertion of a VH gene into the TCRα/δ locus producing a current organization as it is found in zebra finch. (C) Depiction of the inversion/translocation and VHδ gene duplication that yielded the current organization found in frogs. (D) Depiction of the translocation of a VHδ–Dδ–Jδ–Cδ cluster to a location outside the TCRα/δ locus generating a second TCRδ locus as it is currently found in chicken and turkey. (E) Depiction the translocation that took place in mammals giving rise to the TCRµ locus. (F) Loss of TCRµ in placental mammals, loss of D gene segments in cluster encoding the support V domain, retro-transpostion to form a germ-line joined V in marsupials, and duplication of TCRµ clusters in both monotremes and marsupials.