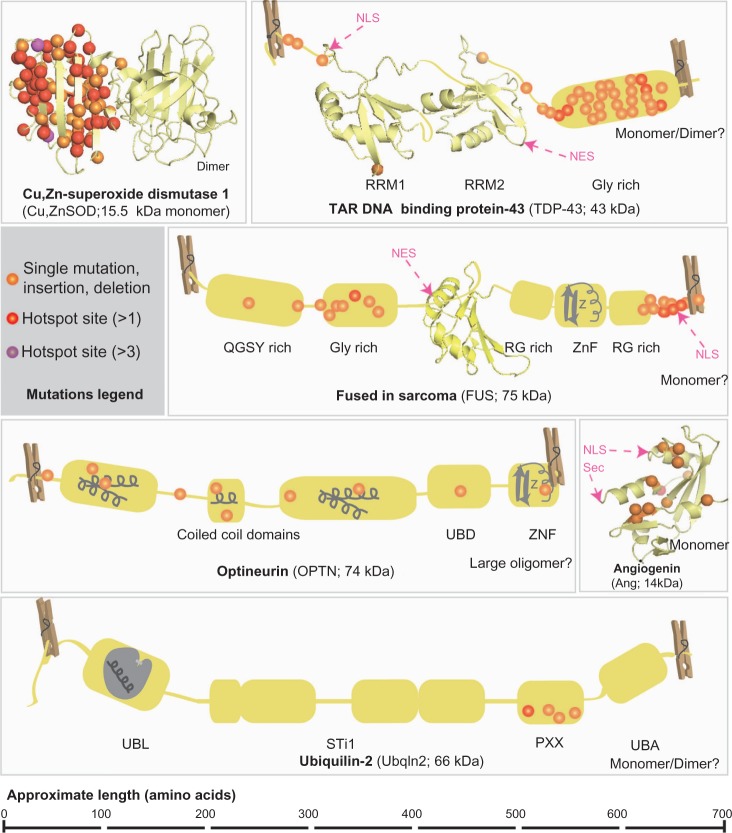
Figure 1.
Known mutations in FALS and SALS-associated proteins.
Notes: Known mutations are mapped onto their corresponding proteins. Single mutations can include point mutations, premature stop codons, deletions, or insertions. For simplicity, one of the SOD dimers contains the mapped mutations. Structural and Domain Organization is indicated. Solved structures of domains or entire proteins are shown as ribbon diagrams: Cu,ZnSOD (1PU0); TDP-43 RRM1 (1CQG); TDP-43 RRM2 (1WF0); FUS RRM (1LA6); Angiogenin (1B1I). Clothespins indicate that the tertiary structure and inter-domain associations are not entirely known, so protein is stretched out to better show mutations sites. Schematic depictions of conserved domains without solved structures are shown in grey. Where applicable, known or putative oligomeric state and molecular weights are indicated.
Abbreviations: FALS, familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; SALS, sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; NLS, nuclear localization sequence; NES, nuclear export sequence; Sec, cleaved signal sequence; RRM, RNA regnition motif; X rich, X (amino acid residue) rich motifs; UBD, ubiquitin binding domain; ZnF, zinc finger; UBL, ubiquitin like domain; STI1, heat-shock-chaperonin-binding motifs; UBA, ubiquitin associated domain.